Keeping yourself updated of the latest cyber
Small businesses represent a major force in the U.S. economy. More than 27 million small businesses in the U.S. generate about 50% of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP). As a business owner, you create opportunities for people to achieve financial success and independence. You also provide jobs for other people.
Small businesses also complement larger businesses. They provide them with services and products to sell. Many small businesses and medium businesses team up with enterprises and sell their products.
They deserve no less when it comes to cyber
Small businesses don’t feel they are prime targets of cyber criminals. Cyber
What is a small business?
Generally, a business is defined by how much money it makes in a year and the number of people it hires. Some business organizations define small business with different sets of criteria.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) defines a small business as one with 50 or fewer employees. The Ohio State University’s National Center for the Middle Market (NCMM) defines it as one with less than $10 million in annual revenue.
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) defines small business as a privately owned sole proprietorship. It may also be a partnership or corporation generating revenue ranging from $1 million to over $40 million. It may have between 100 to over 1,500 workers. This definition varies according to the business’ industry classification.
For purposes of this blog, we will consider the definition of the SBA.
It is important that you know the classification of your business. Government offers benefits your business qualifies for. But you also need to know the regulatory obligations you have to follow in the conduct of your business.
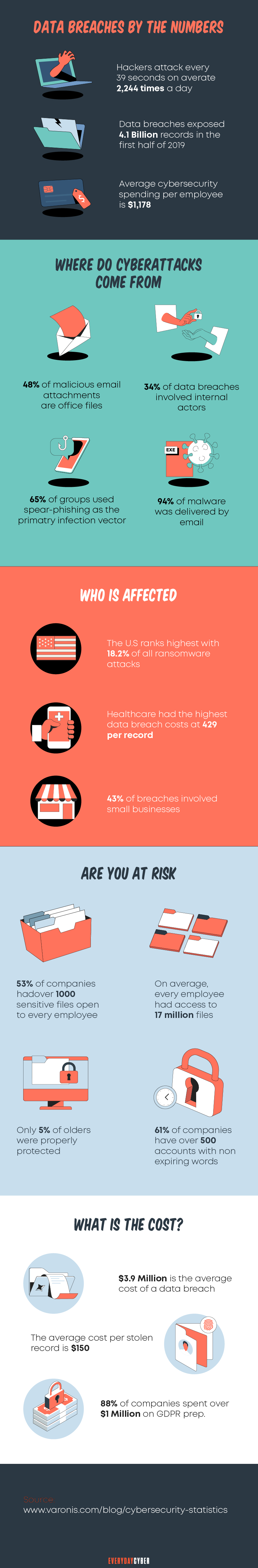
Why are SMBs more vulnerable to cyber attacks?
Cyber attackers are capable of attacking major corporations. So they can more easily attack small businesses. But small businesses think they are unlikely targets of cyber attacks. They think they’re too small to catch the attention of cyber criminals.
That is not the case.
Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) showed otherwise. The report found that one in three breaches involved a small or midsize business. About 60% of these businesses cannot continue doing business within half a year after an attack. This is an alarming consequence.
So why are small and medium businesses so vulnerable to cyber attacks?
Attackers use small businesses as a way to get into the systems of larger corporations
Businesses, big and small, are interconnected with each other. Attackers know this and they leverage this environment. Larger businesses are more difficult to penetrate than smaller businesses. Big businesses have the resources to protect their systems from a cyber attack. A small company’s total spending on cyber
Cyber attackers have found ways to use small businesses to get into the larger systems
They first get through the supply chain, such as third-party contractors. They compromise small businesses that have connections with bigger ones. Then the criminals find their way into the networks of the bigger companies through these smaller companies.
Attackers used this technique in the Target breach of 2013. The attackers first got into HVAC company Fazio Mechanical Services. They did this with a trojan via a phishing attack.
The criminals used the stolen credentials to penetrate the Target network. They probed vulnerable machines to exploit. And they were able to home in on the point of sale network as the weakest point.
They stole 40 million debit and credit card numbers and around 70 million personal records.
Small businesses lack resources to protect themselves from cyber attacks
Many small businesses have no dedicated IT support that handles cyber
Also, KEEPER and the Ponemon Institute published a global risk report on cyber
Covid-19 made the situation worse. Small businesses had to adopt remote work without the proper safeguards. About 40% of those companies reported a 40% increase in cyber attacks.
Small businesses lack security measures for remote work
The pandemic caused the quick adoption of remote work. But small businesses were not prepared due to insufficient resources. They could not cope with new
In fact, there is a 600% increase in malicious emails amid the Coronavirus crisis. And a cyber attack is happening every 39 seconds worldwide.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Common cyber security stats every small business needs to know
We’ve put together some of the latest cyber
1. Small business cyber attacks increased by 424% in 2020
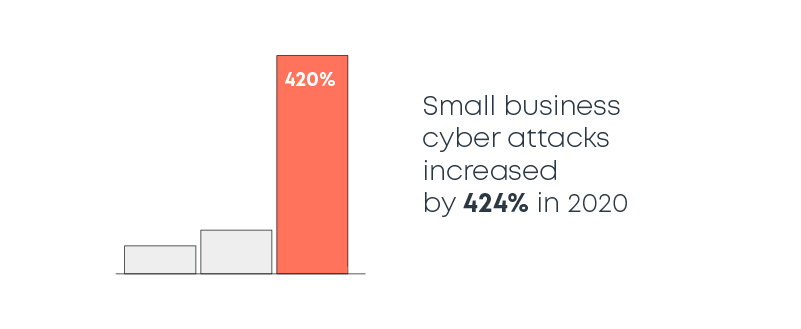
The increase is partly caused by the rush of small businesses to adopt remote working. But they did so without the
Ransomware attacks rose in numbers. Cyber attacks also increased because companies give in to ransom demands. They are willing to pay ransom because they want to get their data and systems back. Small businesses don’t have resources to spend on sophisticated cyber
The rising popularity of cryptocurrency is also driving ransom-based attacks. Criminals prefer cryptocurrency because it is less regulated and harder to trace. It allows more anonymity in transactions that are criminal in nature.
2. About 43% of cyber attacks target small business

The Verizon 2019 Data Breach Investigations Report showed that 43% of small businesses experienced data breaches. Large enterprises are beefing up their cyber
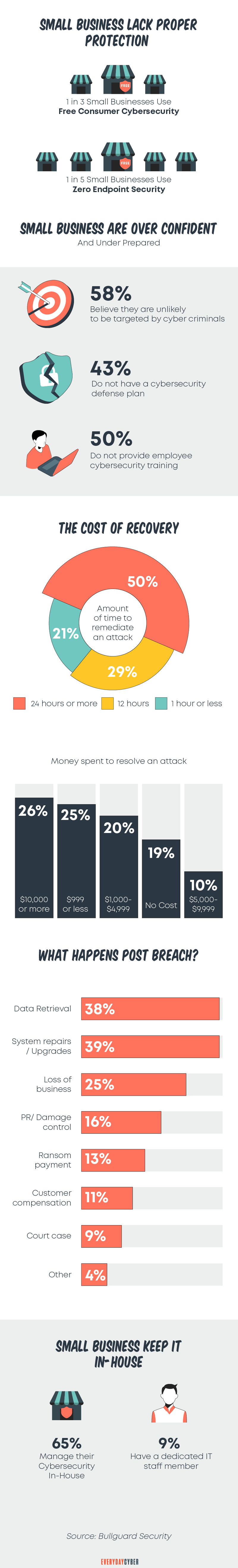
According to a recent BullGuard survey, 58% of small businesses don’t think their businesses are likely targets of attackers. About 43% don’t have a cyber
3. Small businesses spend an average of $7.68 million per insider-related cyber attack

Insiders include employees, partners, and customers doing business with a company. They are the most vulnerable victims in an organization.
An IBM report revealed the cost of insider threats in 2020. The average cost of a cyber attack caused by a negligent insider is $7.68 million per incident. Of the 4,716 incidents reported in 2020, carelessness of insiders caused 2,962 of these.
Remediation costs and fines add to the costs. Downtime is also an expensive consequence. It takes an average of more than two months or 77 days to contain an insider threat.
4. Human error caused a little less than 90% of all data breaches

Employees’ mistakes caused 88% of data breaches. This was reported in a study by
- 34% of male respondents to a phishing email clicked on a malicious link compared to 17% of females
- 57% of remote workers are more distracted when working from home
- 43% of employees click on phishing emails because they think these are legitimate
- 41% of employees open phishing emails because they think they come from trusted sources
5. About 66% of small businesses experienced a cyber attack in 2019

More than two-thirds of respondents encountered a small business cyber threat in 2019. This is revealed in a research report sponsored by Keeper
In the same report, 69% of respondents claim that 61% of the attacks were more targeted and severe. An estimated 60% were sophisticated.
6. 30% of small businesses reported phishing as their top security threat in 2019

Verizon’s 2020 DBIR report reveals phishing is the top
7. 43% of small businesses don’t have a cybersecurity defense plan

A 2020 BullGuard report revealed an alarming number of small businesses in the US and the UK are not ready for a cyber attack. About a third of SMBs with 50 or less employees use free consumer-grade
Small businesses are not exempt from cyber attacks. In fact, they are popular targets because they don’t focus on
8. 70% of small business employees had their passwords stolen

70% of SMBs had their employee passwords stolen or lost in 2019. 63% experienced a data breach caused by a negligent employee, partner, or contractor. And 54% have no idea of their employees’ password practices. These are revealing information from the 2019 Keeper Report.
What do all these data breaches mean? They mean that many businesses are not prioritizing
9. 86% of data breaches against small businesses are motivated by money
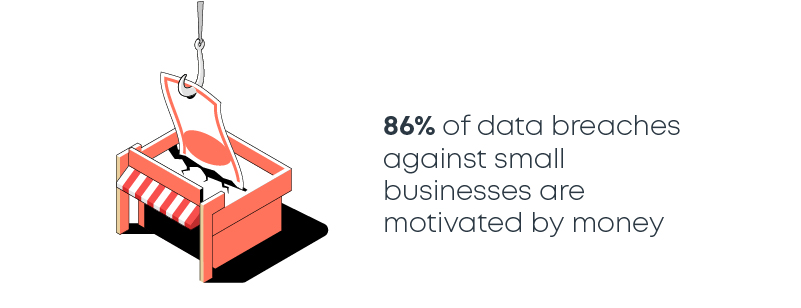
Eight in 10 data breaches are financially motivated. This data comes from the 2020 DBIR report. Criminals also attack small businesses for espionage, grudges, and — get this — for fun.
10. Cloud- and web-based applications were prime targets for cyber attack

The Verizon 2020 data breach report revealed that attackers target small businesses. They use cloud- and web-based applications and tools to launch their attacks. Phishing is the biggest threat for small businesses, followed by stolen credentials. Attackers also target sensitive information, medical records, and financial information.
Why is cyber security important for small businesses?
Cyber
If you’re a small business owner, you don’t have to invest in expensive
Here are the benefits your small business will get from a cyber
Protects your network from cyber attacks
Having a
Develops a cyber security culture in employees
Human error is a major cause of data
Keeps crucial data backed up and protected
Customers entrust their information to companies and they expect them to be safe. You have your own data to protect. Data critical to your business must not be lost. If it is, it must be recovered as soon as possible. Backing up and restoring data is one function of a cyber
Controls access to the network
A good cyber
How can you protect your small business from cyber attacks?
Covid-19 makes safeguarding data all the more challenging. But you need to do it to protect your business and thrive, or at least survive. Here are some of the ways to do that:
- Use firewalls,
antivirus , and endpointsecurity solutions. - Backup your data.
- Encrypt important information.
- Use multi-factor encryption.
- Use two-factor authentication.
- Use passphrases instead of weak passwords and manage them well.
- Restrict use and access to accounts with administrative privileges.
- Monitor use of computer equipment and systems.
- Develop incident response and disaster recovery plans.
- Create, put in place, and monitor cybersecurity policies to guide employees.
- Train your employees to be safe online.
- Consider getting cyber
security insurance. - Get updated on the latest cyber
security news and statistics.
Our final thoughts: The small business sector is a driving force to the economy of a country. As a small business owner, you need to know and analyze cyber
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is Hacking?
Hacking is an old game in the cyberworld with ever changing players and techniques. It may be done with good intentions or malicious motives. It is growing rapidly because of the proliferation of devices.
What is a Website Security Certificate?
A website security certificate is a digital certificate that asserts the identity of a website. It’s a virtual file approved by an industry-trusted third-party called a certificate authority (CA)
What is a Trojan Horse?
Trojan horse computer viruses are malware disguised as or hidden in legitimate software. Hidden from view and ready to attack.
What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted cyberattack to steal your information. You should be aware of the dangers of this and how to address them.
What is Shoulder Surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a form of social engineering that enables cybercriminals to gather information just by looking over their victims’ shoulders. The aim of shoulder surfing is to obtain personal data, such as usernames, passwords or personal identification numbers (PINs), bank account numbers or credit card numbers.
Do You need to Conduct a Cyber Security Risk Assessment
Small businesses experience cyber security risks in varying forms and sophistication every day. Being complacent about the risks and ignoring the importance of a cybersecurity risk assessment can damage the health of their businesses.


