In an analogue environment, identifying yourself is pretty simple. When you go physically to a bank to open an account, book a flight or make an appointment with your dentist, you are usually required to present a valid identification card. The company you are doing business with will want to be sure that you are what you claim to be.
In the digital world, the traditional version of you has a digital
Our daily personal, professional and business lives are ever shifting to digital. Digital
What is Digital Identity ?
There is no single definition of digital
A digital
For example, your online bank account, posts you’ve created, liked or commented on, photos you’ve posted to social media or your browsing preferences are items found online to identify you.
What are digital identifiers?
Your digital
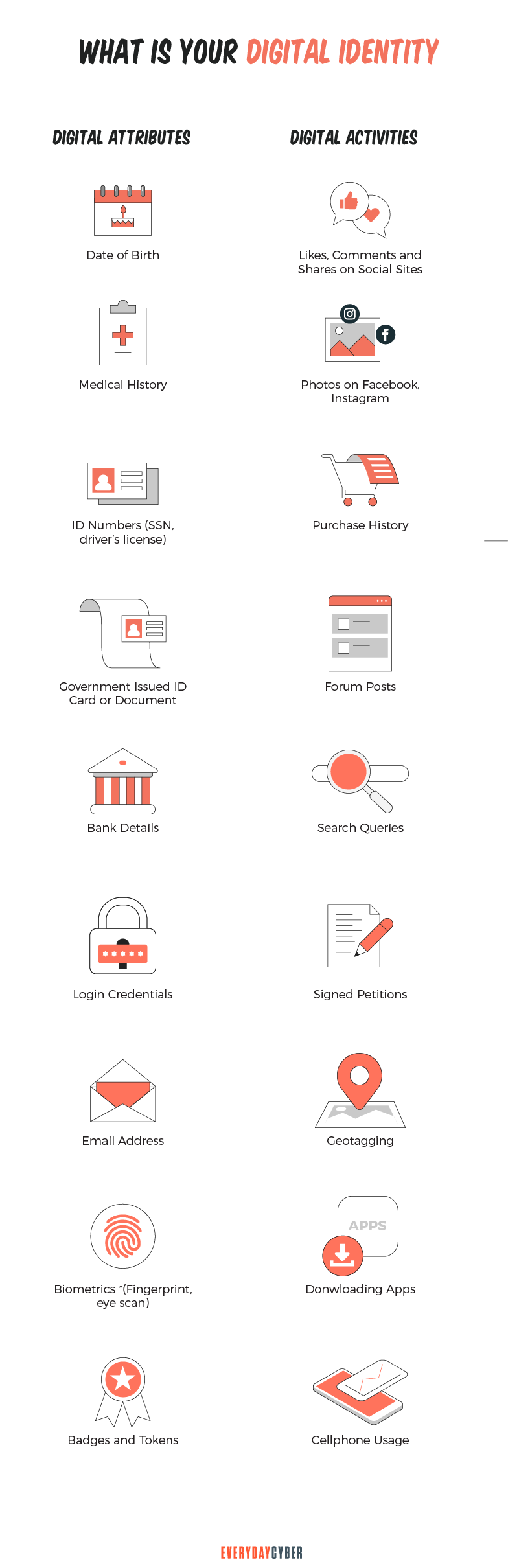
Digital attributes or characteristics are personally identifiable information (PII) found in online records. PII are often used when you’re enrolling in school, applying for a job, or registering a business. They can be any or a combination of the following:
- Date of birth
- Home address
- Email address
- Government-issued ID documents, such as a passport, driver’s license, or Social
Security number - Login credentials to various online accounts
- Biometrics
- Badges or tokens
Digital activities refer to all the things you do online with your mobile, laptop, tablet or any electronic device, such as the following:
- Browsing history
- Uploading photos, posts and comments on social media
- Online selling and shopping
- Doing virtual conferences, meetings, trainings and the like
- Studying online
- Downloading apps
- Uploading videos, blogs or vlogs
- Doing remote work, and many more
What makes up a digital identity ?
We can further break down the two general categories of information that can identify you into context-based characterizations. These interpretations often depend on use cases or the purpose of the digital activity, such as the following
1. Digital identity as credential
Digital
- Name
- Date of birth
- Home address
- Nationality
- Email address
- Valid IDs
2. Digital identity as character
Individuals and organizations shape their online character through the activities they do online. They create and solely control their online profiles from their commentaries, photos they upload and other self-portrayal actions. The information include:
- Social media profiles
- Networking activities
- Career and achievement updates
3. Digital identity as user
This category involves the digital behavior of an individual that reveals habits, interests, preferences and priorities. These actions can be determined from:
- Websites visited
- Email newsletters opened
- Webinar participations
- Online shopping
4. Digital identity as reputation
This concept reveals an individual’s historical data from public records sourced from established authorized third parties. The information includes:
- Degrees, diplomas and other educational achievements
- Employment history
- Credit scores
- Recommendations, citations and testimonials
- Criminal and other court records
The Importance of Digital Identity
Trust is the most important currency in the digital world. Digital
Digital
Similarly, organizations, businesses and governments need trusted digital
What is the value of digital identity ?
Digital identities have no fundamental value on their own. They exist as part of an ecosystem that validates and requires them in all online activities. Their function involves pointing back to specific individuals, organizations or devices. But when they are available in the wild (dark web) the individual elements do have value. Particularly to bad actors.

When used in this context, digital
Digital identity enables certificate authorities to validate you and your organization
Certificate authorities, or CAs, are reputable third-party organizations recognized by the Certification Authority Browser Forum, or CA/Browser Forum, to verify digital identities based on real world information.
Once certified by the CA/Browser Forum, CAs look into official records which include your company name, address, contact details and other company information. They are also responsible for finding other information from outside sources to help them validate your digital
If everything is in order, your CA then issues a website
You know that your TLS/SSL certificate is working to secure your digital

But if you see an exclamation point inside a darkened triangle on the browser, it means the website is not secure, as illustrated below:
Having a verified digital identity allows you to prove to other parties that you are the real you
Having a digital
Without verification, anyone can attempt to impersonate you or your company and trick naïve users into believing the impersonator is you. He or she could set up an imposter website that mimics your website. Or create a fake email account and bogus social media profiles to convince users that those fraudulent accounts belong to you.
In short, verification establishes the legitimacy of your digital
A verified digital identity helps identify and avoid the bad guys
Phishing and other fraudulent online activities have incredibly increased since the start of the covid pandemic. In its Phishing Activity Trends Report for the fourth quarter of 2020, the Anti-Phishing Working Group disclosed that:
- The number of phishing attacks grew and doubled through 2020
- The average amount of wire transfer requests in business email compromise scams increased from $48,000 in the third quarter to $75,000 in the fourth quarter
- Financial institutions, webmails and SaaS sites were the top targets of phishing attacks during the fourth quarter
- Phishers used deceptive techniques to fool users, including using domain names of known brands, using encryption to create a false sense of
security in users, and spoofing email addresses of trusted companies and contacts
For the bad guys, pretending to be a legitimate company is easy — it’s their trade. All they have to do is buy a domain name that resembles the name of a popular brand and get a free domain validation (DV) certificate from a non-profit certificate authority.
Or, steal identities and personal information, with bank account numbers, credit card details and Social
According to the Annual Data Book of 2020 of the Federal Trade Commission, instances of
These and many more
Keep your company network protected with a legitimate digital identity
Your organization’s internal IT system is as important as your website. Keeping an eye on the digital identities of your users and the connected devices in your network can help you detect any suspicious activities taking place on your network. Monitoring these resources helps you mitigate potential network-related compromises and data or
Digital identity helps streamline processes
Protecting the usernames and passwords of your network users can be overwhelming. The storage and management of login credentials can be a cause of disagreement between users and the organization. A centralized digital
A smoother, more secure digital
Digital identity gives customers increased access to products and services
A uniform digital
Digital identity helps improve security
Compromised personal information and account credentials can result in
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
How Digital Identity is Created
A digital
Digital
Step 1: Capturing
An individual’s
Identification documents may include a national ID, passport or driver’s license. Image analytics then extracts the individual’s name, birth date, home address and other relevant data.
Biometric capturing devices include mobile phones, web cameras, tablets, kiosks and specialized fingerprint and facial scanners. These devices are used to capture biometric attributes such as facial recognition, finger and hand geometry recognition, iris recognition and voice recognition.
Step 2: Verifying
The main goal of verification is to confirm the authenticity of an individual’s identification documents and biometrics to validate his or her
After capturing the identification documents and biometrics, the identification system uses dedicated software to compare them to the stored model.
Step 3: Digitalizing
The last step involves the creation of the digital ID after ensuring that there is a match between the individual’s identification documents and biometrics.
Trusted Digital Identity
A digital
People own many digital identities that come in the form of usernames, email addresses, passwords as well as biographic and biometric data. In some cases, such as in social media, some people use pseudonyms to protect their
However, when it comes to critical areas, such banking and government services, people need a trusted digital
A trusted digital
Such rigorous verification and authentication processes make digital identities trusted. And when they are trusted, they enable smoother digital workflows, improved customer experience and reduced operating costs.
Traditional Approaches to Digital Identity Verification are NOT a Guaranty of Cybersecurity
Most businesses use traditional structures and approaches to verifying their customers’ online
- Passwords or
security questions (Something customers know) - Smartphones or special tokens (Something customers have)
- Biometrics (Some that are inherent in customers)
Businesses have been heavily relying on the first two models. These approaches have their own set of vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
Passwords and
Massive data breaches of even giant brands like Yahoo and Facebook have sent hundreds of millions of personal data spilling into the dark web. Things like usernames, passwords, telephone numbers, bank account and credit card numbers, email addresses and credentials, dates of birth and many more are awash in cyberspace.
Modern businesses are now moving toward biometrics for more secure digital
In light of the global nature of cybercrime, providers of
Digital Identity Verification
Digital
In the age of the Internet where the majority of the world is digitally connected, businesses across all industries are gravitating around digital infrastructures to better serve their customers. Digitally
Banks need digital
For travelers, digital
Online sellers and buyers enjoy more convenient and faster transactions using digital
How does digital identity verification work?
The verification process works in several ways. It is usually done by comparing something the person has, such as an identification document or biometric data, with a verified data set, such as government records. Specifically, the methods include the following:
- ID document verification: Verifies that the ID documents are legitimate.
- Biometric verification: Uses selfie technology to determine that the individual presenting the ID is the same individual whose photo appears on the ID.
- One-time password verification: Sends an OTP via SMS or email to the applicant during the verification process.
- Knowledge-based authentication: Asks “out of wallet” questions taken from the applicant’s personal files stored in various databasess. If the applicant is a legitimate individual, the answers to the questions will be easy. If the applicant is a fake, he or she will give the wrong answers.
- Trusted
identity network: Refers the applicant’s submitted credentials to other established entities, such as a past service provider, to check if the information submitted matches those with the provider. - Database verification: Leverages data from offline databases, social media, government records and other sources to cross-check the information submitted.
- Liveness detection: Liveness detection is a verification method using artificial intelligence software to determine if the computer is interfacing with a live human, and not a robot, spoofed thing or injected video or portrait.
Digital Identity Management
Digital
A comprehensive approach to digital
From a cybersecurity point of view, managing digital identities enables organizations to take control of access to company data. This means that only authorized personnel should have access to information depending on their role in the company. The cybersecurity team may be given more access than the customer service staff. Customers should be given quick access to what they need in a secure environment. But low-level and high-risk users should be limited to information that matches their roles.
Potential Threats to Digital Identity
Identity theft is the most common threat to digital
People use their digital identities for almost everything they do in their daily lives. They use them when they access their bank accounts, visit their healthcare providers or chat with their friends on social media. They do all these in cyberspace where prying eyes are eagerly waiting to steal their personal information.
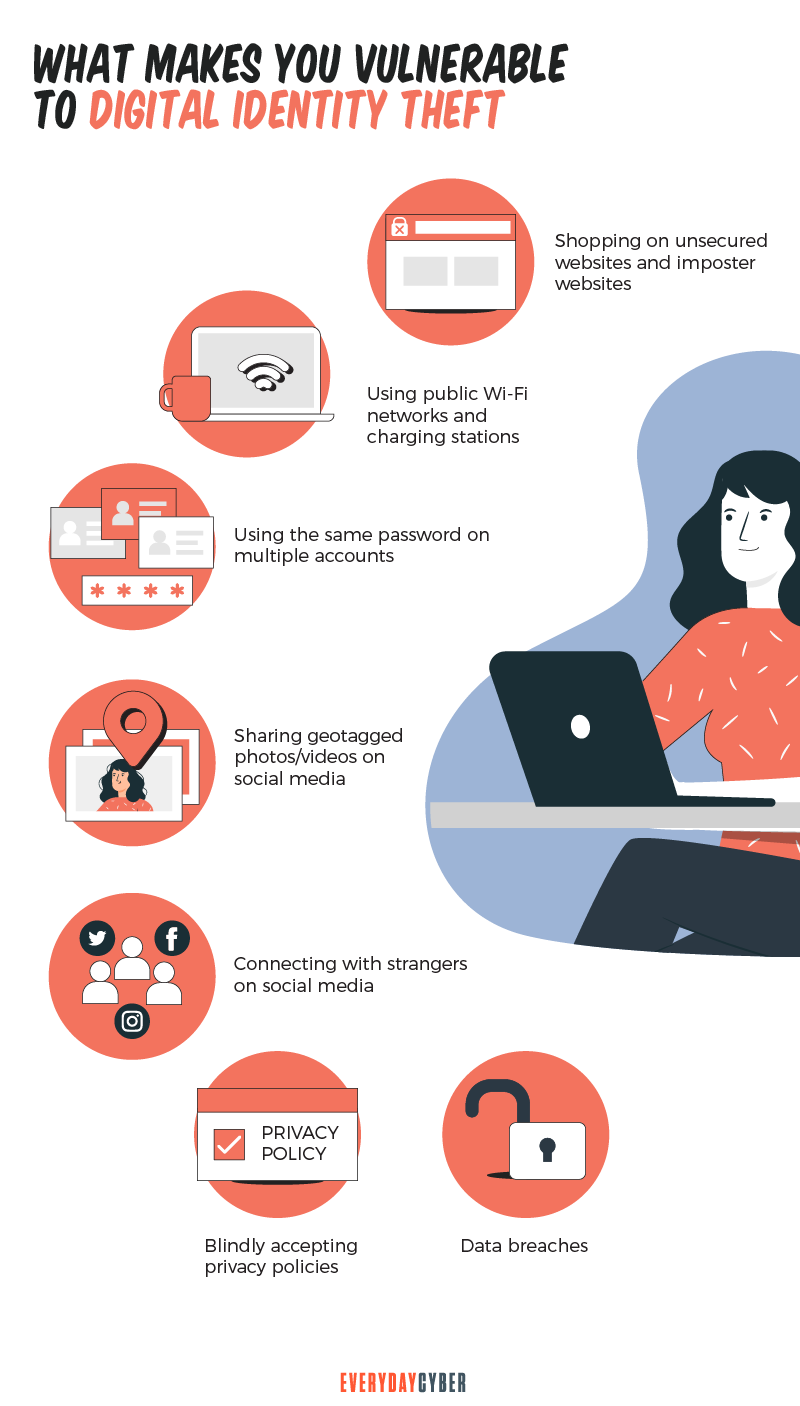
And how is digital information exposed? It happens in many vulnerable places, such as:
- Unsecured websites
- Public Wi-Fi networks
- Phishing emails
- Weak passwords
- Third-party data breaches
- Downloading malware-infected apps
- Adding strangers to social media accounts
Hackers know where to look and they have a vibrant market where they can dump their hacks. — the dark web. Social
How can you protect yourself from identity theft?
Every time you go online, you provide your personal information to access the accounts you need. If you do this in an insecure environment, you’re opening yourself to vulnerabilities that criminals can exploit.
However, there are ways to protect yourself from
Always use strong passwords
To make it strong, use a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers and symbols. Make it long to at least 15 characters. Avoid common substitutions, such as WH337 for WHEEL and don’t use sequential keyboard paths, such as qwerty. In short, create a password with random character placement.
Never provide personal or financial information
Your trusted bank will never ask for your bank account number. Your service provider will never ask your account name. Your employer will never ask how much salary you’re receiving. The reason is common sense. They already know all this information about you. So if someone purports to be them asks, you should be suspicious.
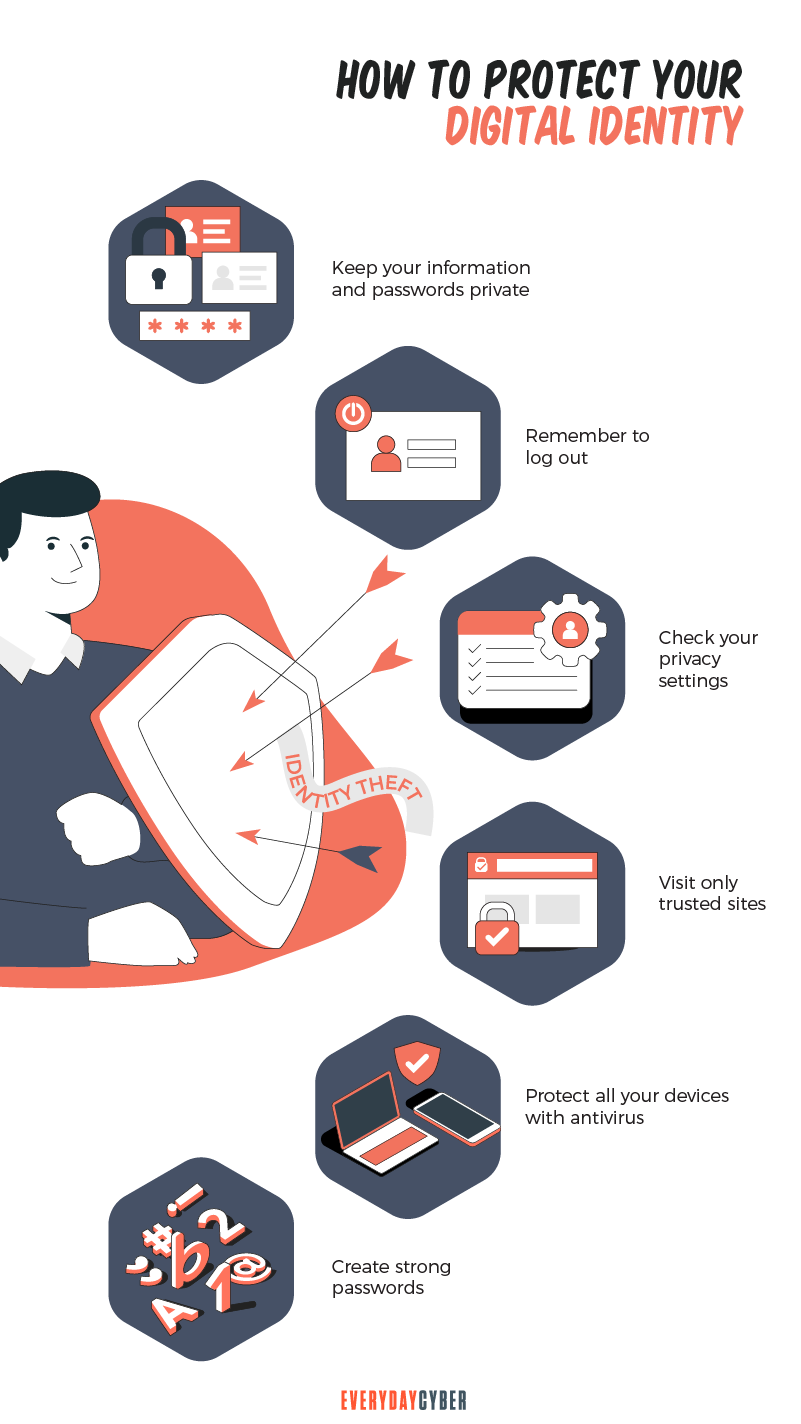
Avoid downloading software from unknown websites
It is often tempting to download software that promise sweet little things or pop ups that offer great deals. These may actually be programs that contain malware that can steal your
Never post personal information online
You should keep your date and place of birth, address, names of family members and other sensitive information to yourself, especially on social media networking sites. These are breeding grounds for hackers to perpetrate their evil schemes.
Don’t leave a paper trail of your financial transactions
Shred credit card, banking transactions and other financial documents with sensitive personal and financial information. Nor leave them on your office desk or throw them into the waste bin unshredded. Don’t keep your Social
Monitor your credit
Credit card theft is the most common cyber theft because of the massive data branches that are happening worldwide. Check your credit card statement for any unknown activities or inaccuracies. Make sure you recognize the purchases, merchants, locations and other related information. If there are any discrepancies, immediately report them to your credit card company.
Use antivirus and antimalware software as often as possible
Antivirus and anti-malware software help detect, flag and remove viruses and malware. The software contains a database of all known viruses and malware. Once it detects any, the software isolates and removes them.
How to Use Digital Identity to Protect Your Business
Nowadays, more employees are working remotely and more individuals are doing business almost entirely online. This means good business, but it also means more digital identities to manage securely.
The worst fear of every e-commerce business is having someone mimic their website. When this happens, it’s bad enough that businesses lose customers, but it is even worse because they’re losing their reputation, too. And what does this mean if the trend is unchecked? Loss of income, or closure of business all together.
Here are positive ways companies can leverage to protect their business:
#1. Install TLS/SSL certificate on your website
A TLS/SSL certificate is a website
#2. Use email signing certificates
An email signing certificate is a digital file that allows users to digitally sign their email communications. It also enables users to encrypt the email content and all attachments included in them. It authenticates the
#3. Use PKI client authentication
PKI, or public key infrastructure, is a technology for authenticating users and devices. It certifies that a particular cryptographic key belongs to a specific user or device. So that if a cybercriminal attempts to penetrate a system, the PKI client authentication tool will block it, keeping the business safe.
#4. Train employees to verify digital identity
Frontline employees need to be trained, and trained properly, to verify digital
Our Final Thoughts
An effective digital
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
5 Biggest Cybersecurity Mistake SMBs do
Small and midsize companies can’t afford to learn cybersecurity haphazardly while cyberattacks are steadily rising. If you’re a decision-maker, you can’t ignore the 424% increase in cyber breaches in 2021.
A Step-by-Step Process for Creating an SMB Cybersecurity Plan
Failing to plan is a plan to fail. The vulnerability of your small business's digital infrastructure is dramatically increased without a sound cyber security plan. Business plans help achieve desirable outcomes. You don't want to be a cyber attack victim, so build a plan.
What is Bloatware?
Preinstalled and unwelcome. Bloatware is unwanted software installed on your digital device; slowing it down, reducing battery life, consuming space and just destabilizing it.
What is a Computer Worm?
A computer worm is not a cute, squiggly little creature. It is an evil, malicious piece of software destined to wreak chaos and disaster on many devices.
What is a Rogue Certificate?
A rogue certificate is a valid certificate issued by a legitimate certificate authority. However, it’s untrustworthy because either it was compromised or was issued to the wrong party.
What is Pharming?
Pharming is cybercriminals “slight of hand” cyber attack. Redirecting you to a fake website imitating a legitimate site so they can steal your login info, financial data, and more.


