Virtual private networks (VPNs) are growing in popularity and usage worldwide. People use them in their homes, offices or businesses for a variety of reasons but mainly for privacy and
So what is a VPN
A
When you go to a website via the Internet, your computer connects to a remote private server which fetches the data you need from the Internet. The direct source of your data is the
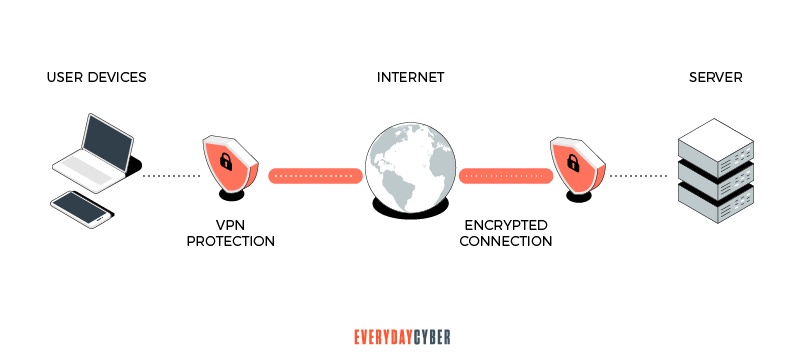
What does a VPN shield?
Since your connection is virtual, you are effectively out of the public eye when you use a

Here they are:
Your IP address
Think of your IP address as your home address. Your home address leads people to your home while your IP address leads them to you and your devices. A
Your search history
Chances are your Internet Service Provider (ISP) has recorded the websites you have searched. A
If you use a
Your geolocation
Geolocation refers to the use of GPS, IP address or other location technologies to track the whereabouts of connected devices identifiable to their owners. A
For example, if you have a streaming service subscription and you are in another country, you can use your
Your personally identifiable information
A
Your devices
Your devices may include your laptop, desk top, tablet and smartphone. They can be juicy targets for cyber criminals when you access a public Internet connection. A
What are VPN protocols?
VPNs connect private networks and a public network, such as the Internet, by creating tunnels.
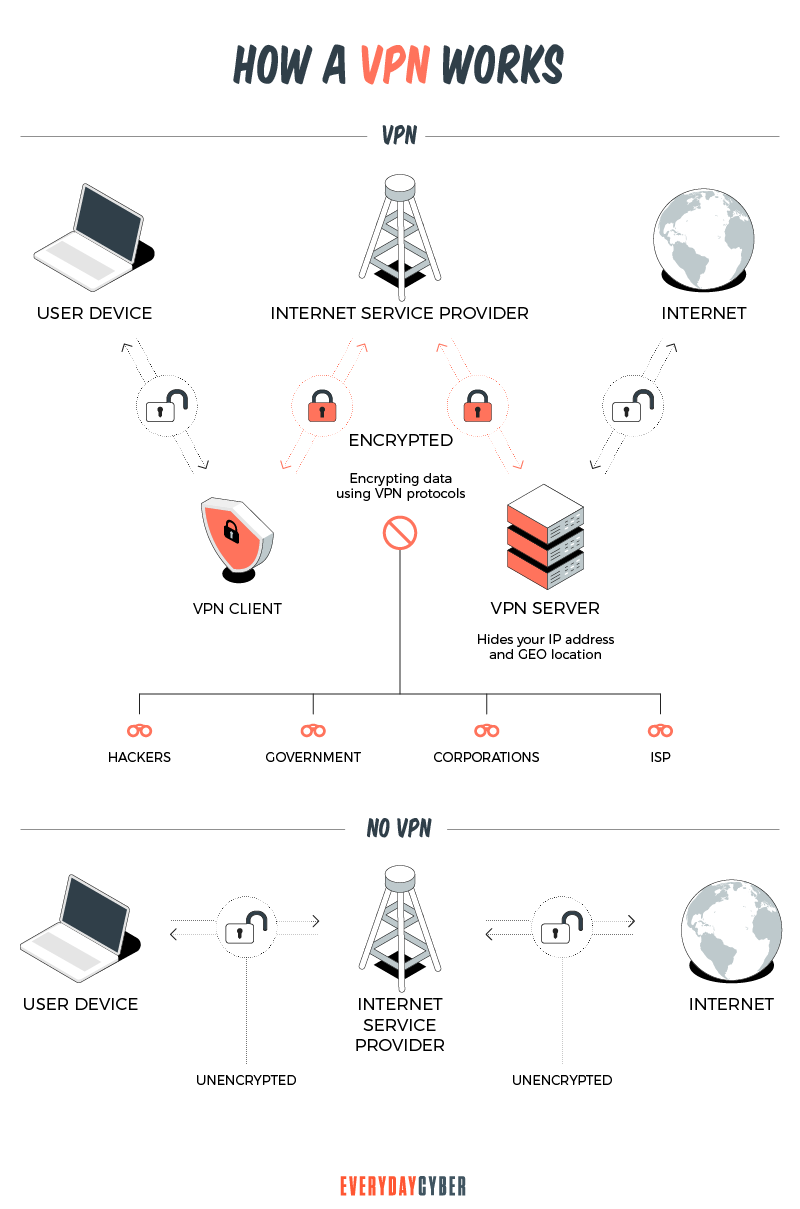
Following are common
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN
The main focus of an SSL
- Secure remote access via a web portal
- Network-level access between the client and corporate network
SSL
Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site
For example, a company that has offices in New York, Los Angeles and Seattle can use a site-to-site
Client-to-Server VPN
A client-to-server
A
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is one of the earliest
PPTPs offer lower costs on transmission, hardware and administrative overhead. It can also deliver one of the fastest connections for users who do not require heavy encryption.
Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol (L2TP)
L2TP is an extension of the PPTP protocol. It is a computer networking protocol provided by many ISPs to enable
IPSec is a set of protocols that authenticates all data communications over an IP network. It operates in two modes: the transport mode and the tunnel mode. When operating under the transport mode, IPSec prompts the source and destination hosts to perform all cryptographic functions. The tunnel mode uses special gateways to perform cryptographic processing in addition to the source and host destinations.
L2TP uses two tunnels: the voluntary tunnel and the compulsory tunnel. A voluntary tunnel allows the remote user to initiate the connection and sends the L2TP packets to the ISP which in turn sends them to the corporate network. In a compulsory tunnel, the remote
OpenVPN
An OpenVPN is an open source protocol that uses
OpenVPN performs encryption and authentication via the OpenSSL library. This is a library for applications that secure communications over computer networks to protect the
OpenVPN uses either of two transport layer protocols to transmit data: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). TCP is a more secure protocol because it allows error correction and waits for confirmation before sending a new packet or sending a packet again. UDP does not perform error correction, allowing for faster transmission.
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
SSTP is a
SSTP transmits point-to-point traffic and it does so through SSL/TLS channels. SSL or Secure Sockets Layer is the standard technology for keeping Internet connections secure. TLS or Transport Layer
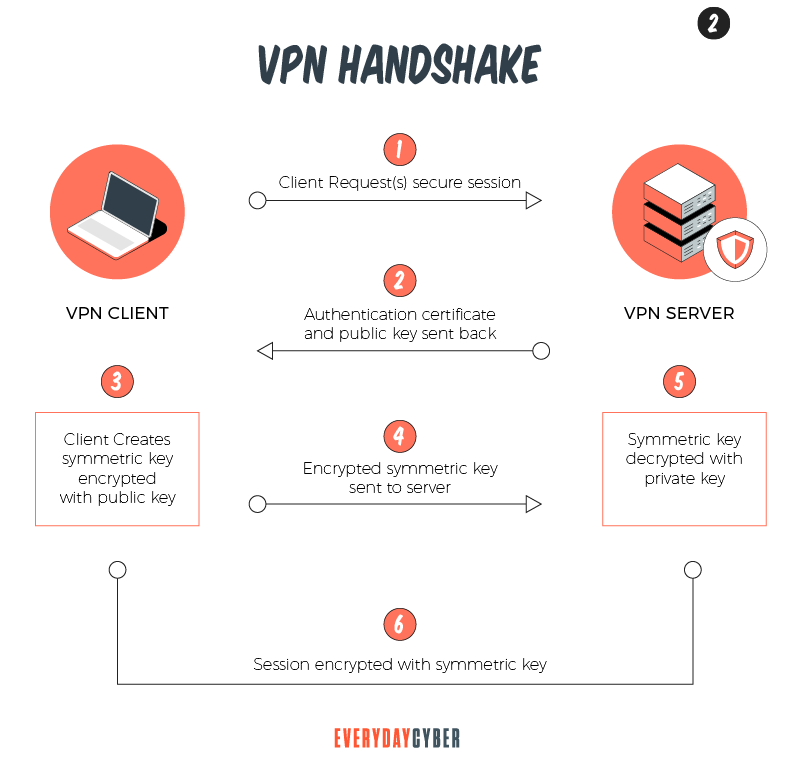
Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2)
IKEv2 is a
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
VPNs vs Proxy Servers
VPNs and proxy servers can help keep your activity private when browsing the internet, sending emails, streaming video, viewing social media and downloading files. But they operate differently and offer a user different values.
Proxy servers sit between you and the server or website you are trying to access, acting as a gateway to the internet. When you connect to a specific website, online service, or app from your computer, laptop, smart
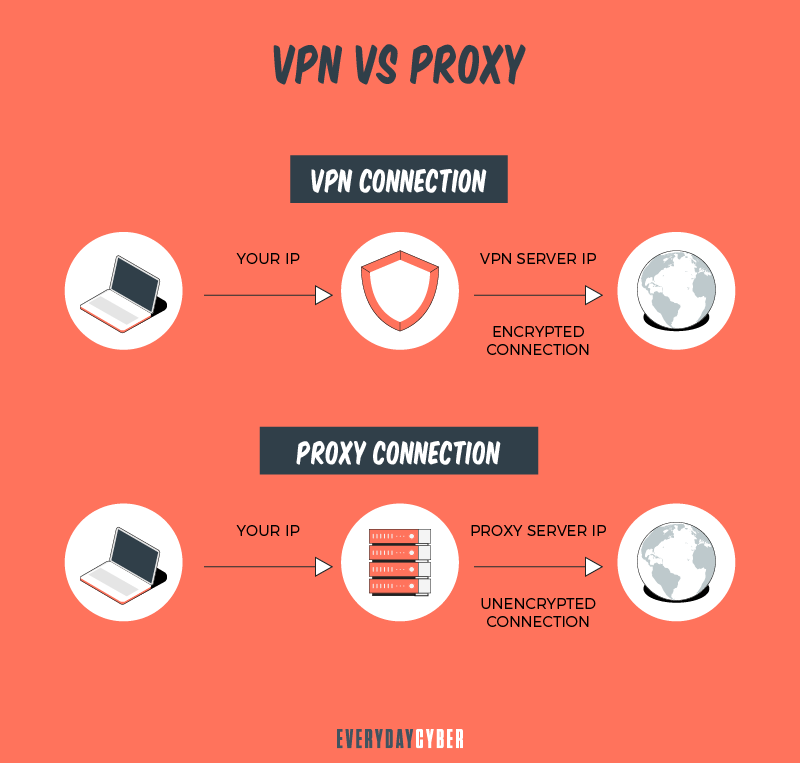
The benefit to this, is that you are able to hide your
The three (3) the most common proxies are.
HTTP proxies
These proxies are used to access websites. They can also be used to access geo-restricted content because the IP address of the proxy server is in the correct geo-location for the service, even though your computer’s address is not. Keep in mind, this may violate the user agreement with your content provider so be aware.
SOCKS5 proxies
SOCKS5 proxies are generally used to access video streaming services, file-sharing sites, or online games. They don’t work with websites. SOCKS5 proxies, which are often free, are typically slower because free proxies generally have less configuration options, support, and slower infrastructure.
Transparent proxies
Transparent proxies are typically deployed by employers, parents, and public facilities like schools or libraries. The are intentionally transparent because the entity that set them up doesn’t really want you to know they are there. Typically they are enabled because there is a desire (limit restricted content) or need (regulatory) to filter user’s content when those users connect to the internet through their networks.
VPNs are similar to proxies, but they work with all access to external networks (internet) instead of just working with single apps or websites.
Like proxies, when you access a website after first logging into a
How VPNs and Proxies differ
1. VPNs encrypt your information
VPNs encrypt your traffic when you’re browsing and any data you send or receive, will be protected. This is important: It means that hackers, government agencies, businesses, or anyone else won’t be able to see what you’re doing when online. Proxy servers do not encrypt their traffic.
2. VPN providers promote online privacy
Most
3. Free proxy connections can be slower
Proxy servers and VPNs can slow down your browsing, depending on how many users are accessing their services. Free proxy connections are notoriously slow and often less secure because they have less support, offer less configuration options, and typically run on slower infrastructure.
4. You may spend more with a VPN
There are free VPNs. But using a
Do you need a proxy if you have a VPN ?
The answer is “no”.
What to look for in a VPN
Choosing a

There are many differences between VPNs. It is your
Here are five things to consider when you buy a
1. Security and privacy
Obviously, these are what VPNs are for. You will want to be anonymous online and surf the web freely. Many VPNs boast of their amazing
It pays to assess the features a
Following are some tips to remember when you are looking for a
Choose the best VPN protocol that suits your needs
The best
For example, the OpenVPN uses
Enable the kill switch by default
Many unexpected things can happen. A server can go down, for instance. If this happens and your
Test for leaks
It is important that your
You can check if your provider has any DNS or IP leak problems by going to ipleak.net. You should also make sure that IPv6 is disabled to prevent your
Check the log policies
A trusted
2. Speed
Of course, we all want a speedy connection without compromising
Speed boils down to the quality, number and location of servers your
3. Ease of use and versatility
You don’t have to be a tech expert to use your virtual private network. Your chosen
Another factor you should look for in a
4. Strong encryption protocols
A
Aside from keeping your
5. Around-the-clock customer service support
Customer service is important to
How much does a VPN cost?
The cheapest or most expensive may not always be the best. But definitely, you will want to get the best
VPN pricing depends on many factors, such as:
- Data usage volume
- Number of devices covered
- Number and types of
security services - Number, location and capabilities of servers you can connect to
- Length of contract
- And more
VPN prices can range from $10 to over $100 and most
Free VPNs are available, but many experts say they rarely work. The risks and problems are way too many. For example, some free
In conclusion, hiding our identity and all the things we do on the Internet is an entirely reasonable concern considering the malicious forces out to encroach on our privacy. We can depend on a virtual private network to do this for us and making the right VPN choice is key to a secure and safe online experience.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is Shoulder Surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a form of social engineering that enables cybercriminals to gather information just by looking over their victims’ shoulders. The aim of shoulder surfing is to obtain personal data, such as usernames, passwords or personal identification numbers (PINs), bank account numbers or credit card numbers.
10 Cyber Security Stats Every Small Business Needs to Know
Knowing the right cyber security stats helps your business fight off and recover from cyber attacks. Get informed.
What is a Drive By Download?
A "drive by download" is a cyber attack where visiting a website or hovering over an Ad causes malware to infect your computer or device.
A 10 Step Plan for Small Business Cyber Security
An effective cyber security plan outlines in simple language the best cybersecurity practices your organization needs to stay safe. It doesn't have to be complicated, but it should be pragmatic.
What to Do if You’ve Fallen Victim to a Phishing Attack
Cybercriminals target phishing scam attempts on fatigued workers in the hopes of catching them off guard with an attention-getting email. They also launch phishing schemes against unsuspecting individual users by using fear and intimidation. And it sometimes works.
What is Hacking?
Hacking is an old game in the cyberworld with ever changing players and techniques. It may be done with good intentions or malicious motives. It is growing rapidly because of the proliferation of devices.

