By now, you may be familiar with Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, or Google’s Google Assistant. Or the pop-up features on websites that ask answers to common questions.
Thanks to the magic of artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots are here to make both brand and consumer’s lives easier and more fun. Brands use them to promote their businesses. Consumers use chatbots to help them with shopping, banking, meal delivery, healthcare, and many other tasks.
If you’re a brand, is your customer service department or call center struggling to answer the same questions again and again? This is a pressing issue that calls for the use of chatbots.
Chatbots learn how to converse with customers in a human-like manner and direct them along the quickest road to conversion. This allows your company to effectively mimic in-store assistance scenarios for digital interactions.
Chatbots also give automated support 24 hours a day, seven days a week, allowing worldwide shoppers to obtain real-time customer service.
Chatbot Statistics
Chatbot demand is rising. What does the chatbot adoption rate look like in 2022 and the near future? What are some of the most eye-catching chatbot statistics that will help you decide whether or not to invest in the technology for your own company?
Here are some of them:
- By 2022, spending on artificial intelligence systems will have risen to $77.6 billion.
- By 2022, chatbots will have helped firms save $11 billion.
- In 2022, 70% of white-collar professionals will interact with chatbots.
- Chatbots are expected to enhance user satisfaction by 80% over non-chatbot buying experiences.
- Chatbots will automate 90% of client inquiries
- 65% of users prefer to ask questions using chatbots
- 70% of respondents said they had a great experience with chatbots
So, What are Chatbots?
A chatbot is an artificial intelligence (AI) software that can imitate a natural language conversation (or chat) with a human user via messaging apps, websites, mobile apps, or the telephone. It allows people to communicate with digital devices as if they were talking to a real person.
Chatbots can be as simple as one-line scripts that respond to a simple query. They can also be as sophisticated as digital assistants, which learn to provide answers to more complicated questions. They can gather and analyze more data to provide greater personal levels of communicating with humans.
Artificial intelligence is the foundation of chatbots. Modern chatbots use the two branches of AI namely, natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML).
Natural language processing is a branch of artificial intelligence that aims to make human language understandable to machines. To explore the norms and structure of language, NLP combines the power of linguistics and computer science. The goal is to develop intelligent systems that can comprehend, analyze, and extract meaning from text and speech.
Machine learning is another branch of artificial intelligence that allows machines to learn without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning creates computer programs that can access data used by machines to learn for themselves.
Chatbot evolution – from ELIZA to ALEXA
People’s fantasies about artificial intelligence started to dwindle when British mathematician Alan Turing created the Turing Test in 1950. The test determines whether a computer can think. Alan Turing proposed the idea that the human brain is a digital computing mechanism that evolves into a universal machine over time.
Researchers continued to work on what we now know as chatbots after Turing’s death. To create the most artificial human experience, they used a variety of technologies such as NLP and AI. By the mid-1960’s, IBM created ELIZA, an ancestor of chatbot technology today. ELIZA seemed to be talking to humans like a real person through computers.
In the early 1970’s, American psychiatrist and AI expert Kenneth Colby built PARRY using the underlying principles of ELIZA. In 1973, ELIZA and PARRY started to converse.
The following years saw some significant chatbot technology breakthroughs in the following creations: [6]
- 1988 – Jabberwacky
- 1992 – Dr. Sbaitso
- 1995 – ALICE (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity)
- 2001 – SmartChild
- 2010 – Siri
- 2012 – Google Now
- 2014 – Cortana
- 2012 – Alexa
- 2016 – Facebook Chatbots (with over 300,000 operating across its platforms as of 2018)
- 2017 – Google Assistant
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Types of Chatbots
To understand how chatbots work, let’s take a look at the different types of chatbots. Chatbots are classified according to build and function.
Types of chatbots according to how they are built
Rule-based chatbots
Rule-based chatbots rely on a set of predetermined rules to tell them how to automatically answer FAQs in the absence of a human.
Rule-based chatbots are relatively simple to develop and train to communicate with customers. The disadvantage is that they are limited in how they may engage in useful dialogue with shoppers because they are programmed using particular rule-based responses.
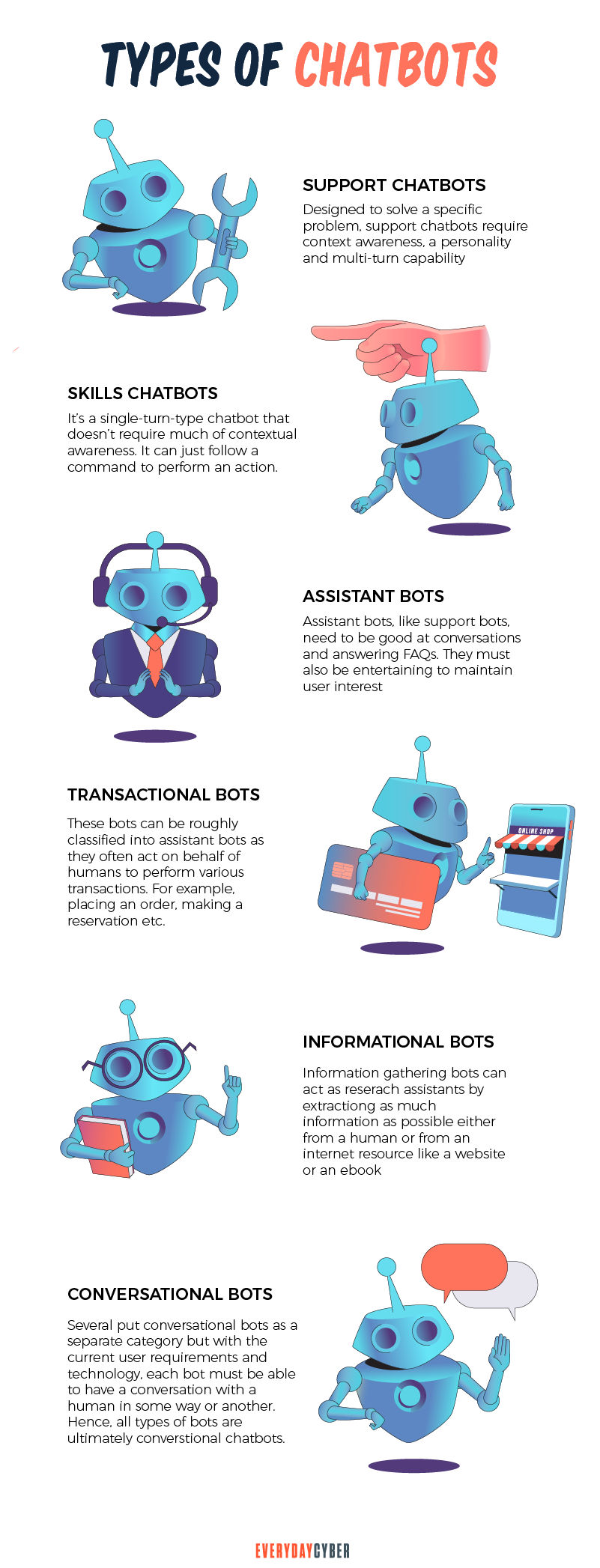
AI chatbots
Modern AI chatbots are driven by artificial intelligence and its two branches – natural language processing and machine learning.
AI Chatbots are a brand’s first point of contact with customers. They let businesses deliver real-time customer help in order to improve service quality and increase repeat business.
Shoppers can receive proactive recommendations from AI chatbots based on their browsing habits. These intelligent chatbots can make recommendations for products that meet the demands of their customers.
Types of AI chatbots according to function
Task-oriented chatbots
Task-oriented chatbots are one-purpose programs that specialize in a single task. They provide automated but conversational responses to user inquiries. These chatbot interactions are quite specific and structured. They’re best used for customer service and support services like interactive FAQs.
These chatbots can execute simple transactions and answer common questions, such as inquiries about business hours. Though they use NLP to engage customers in a conversational manner, their capabilities are very limited. These are the most popular chatbots right now.
Conversational chatbots
Conversational chatbots are also known as virtual assistants or digital assistants. They are more sophisticated, interactive, and individualized.
These chatbots are data-driven and use NLP and ML to learn as they go. They employ analytics and predictive intelligence to provide personalization based on user profiles and previous interactions.
Conversational chatbots can learn a user’s preferences over time, make suggestions, and even predict needs. They can initiate dialogues in addition to monitoring data and intent. Consumer-oriented, data-driven, predictive chatbots include Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa.
How Chatbots Work
We now know the different types of chatbots and their capabilities. When a chatbot interacts with a customer, it performs two tasks:
1. Analyze the user’s request
Collecting user data is a crucial function of chatbots. To engage the chatbot and start a discussion, you’ll often need to provide your first and last name, email address, and
A sales chatbot may inquire into a potential customer’s size, color preferences, price ranges, and other relevant information.
For example, is the item for a special occasion? Is it a car add-on? Or a present for someone special? During a sales session with the AI chatbot, a significant amount of personal information could be exchanged.
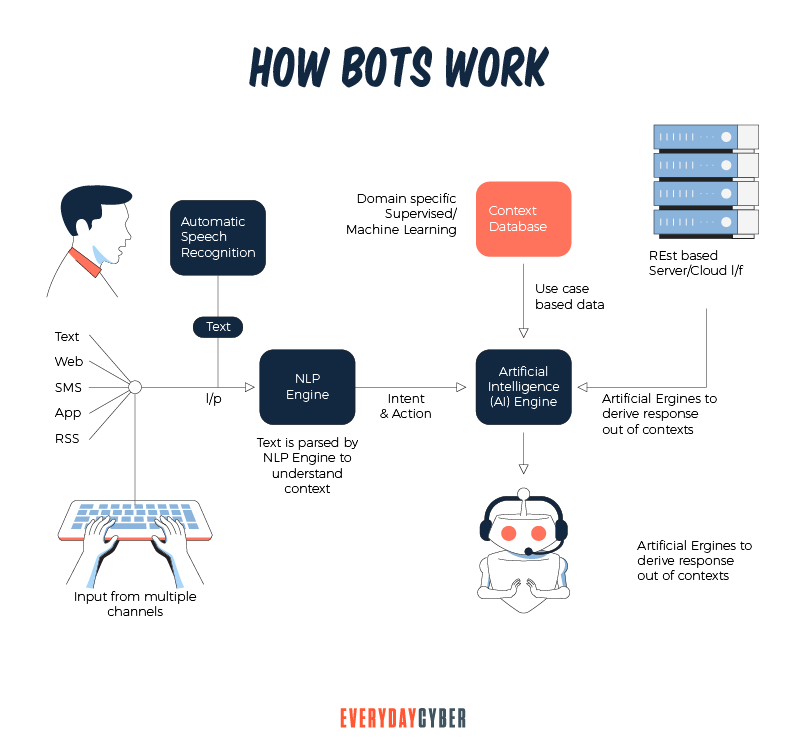
2. Provide an appropriate response
The chatbot must then deliver the most appropriate response to the user’s request once the user’s purpose has been established. Any of the following is a possible response:
- A general and predetermined answer
- Information pulled from a knowledge base that provides a variety of replies
- Information that has been contextualized depending on data provided by the user
- Data kept in business systems
- Information as a result of an interaction between the chatbot and a backend application
- A clarifying inquiry that aids the chatbot’s understanding of the user’s request
Can Chatbots Go Rogue?
(Tay image idea source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tay_(bot))
In general, chatbots have not been used for hacking objectives. Chatbots are conversational assistants that automate repetitive chores. People like them because they assist them in completing jobs swiftly and without the need for human interaction.
However, an unprotected chatbot can be a
Is it possible for a chatbot to carry out a man-in-the-middle attack? A chatbot can be designed to appear as if it came from a reputable company. When a user interacts with the bot, he or she may be asked to share sensitive information. The malicious chatbot may also instruct clients to perform certain actions, such as clicking a link that contains a malware-infected application.
Chatbot hacking can also create “evil” chatbots. Competition between companies is reaching a high level. In order to destroy an opponent in the industry, one might end up hacking a chatbot and turn it into an evil one.
Remember Microsoft’s Tay? It absorbed everything it learned, including the negative ones. It became a racist and anti-Semitic chatbot, which forced Microsoft to take it down.
Chatbot Security Risks
Threats
Threats are one-time occurrences that include malware and DDoS attacks. Targeted attacks against your business can lock you out of your system and be held for ransom. Hackers can also threaten to expose supposedly secure client data. Common specific chatbot
- Ransomware
- Data theft
- Data alteration
- Malware
- Phishing
- Social engineering
- Impersonation
- Chatbot hacking
Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are flaws in the system that allow hackers to get access and expose companies to
- Not using HTTPS protocol
- Unencrypted data at rest and in transit
- Weaknesses of hosting platforms
- Back-door access by hackers
- Lack of
security protocols for employees
What Happens When Hackers Attack Chatbots?
While there are many benefits that businesses can enjoy by embracing chatbot technology, unprotected chatbots are themselves
Chatbots serve as virtual agents for businesses. But they could be
When a representative from a reputable organization says, “Log in and follow this link”, the victim follows unsuspectingly. When the dating app Tinder was hacked, for example, fraudsters impersonated a woman using a chatbot. This malicious chatbot encouraged users to provide their payment card information to become verified on the platform.
Here are common ways malicious chatbots can cause
Data theft
Chatbot attacks can result in data theft. Malicious intent can be used to modify some models. A consumer interacting with a financial chatbot, for example, could be provided a malicious link that redirects them to another webpage where credentials can be stolen. Naturally, fraudulent transactions can follow.
Dissatisfaction of customers
Chatbots can be tampered with in such a way that the user’s purpose or request is misinterpreted, resulting in an inaccurate response. Customers may get dissatisfied and frustrated as a result of this. Even worse, it could cause the system to completely fail, causing major issues with client retention.
Why Chatbot Security is Important
The “https” at the beginning of a website’s URL denotes secure sockets layer (SSL)
Visitors can be certain that their credit card and personal information are safe online by looking for padlock or shield icons in e-payment websites.
There is no such
How to Improve Chatbot Security
To safeguard shared data and protect their clients, system administrators and network managers should consider the following chatbot
Data encryption
Chatbot
If hackers or other unauthorized users walk about your network or website without permission, encryption prohibits them from viewing data. It also stops them from using the data if they are able to exfiltrate it as a result of a data breach.
Authentication and authorization
Two of the most effective chatbot
Authentication verifies user
Among the specific
- Biometric authentication
- Two-factor authentication
- Multi-factor authentication
- User ID
- Authentication timeouts

Website SSL/TLS security
Chatbot
Individuals, devices, and programs cannot access data because it’s transmitted across an encrypted connection. The content of the chat is decrypted using mathematical formulas or algorithms, which are transparent to the end-user.
Self-destructing message
Self-destructing messages are a practical option in many situations when sensitive data is conveyed. Messages containing personally identifiable information (PII) are automatically deleted once a certain amount of time has passed.
Both the user and the chatbot can be involved in the process. For financial and healthcare chatbots, self-destructing messages are an important
Using secure processes and protocols
The HTTPS protocol and SSL/TLS certificate are the default settings for every
These solutions communicate with platforms that already have their own
Data storage
Companies store chatbot data for an analysis of the service. Chatbot developers analyze communications to improve a chatbot’s quality. Machine learning methods need the data to further train chatbots. The quality of chatbot service generally grows with the amount of data.
The best thing to do is to store such information in a secure place for a certain amount of time and to discard them at a later time.
Access controls
User
It’s also a good idea to set a session time limit. If the user walks away from his computer, takes a
Two-factor authentication can be used to add extra protection to chatbot
User behavioral analytics
User behavioral analytics is a
Education for both employees and customers
Because human error is one of the most common sources of cybercrime, it is critical to educate people about chatbot
Customers and staff are still the most vulnerable to mistakes. Unless everyone is taught on how to use conversational chatbots safely,
A successful chatbot
Even if you are unable to train a customer, you can still provide a roadmap or directions for navigating your systems to prevent further
How to Test Chatbot Security
There are
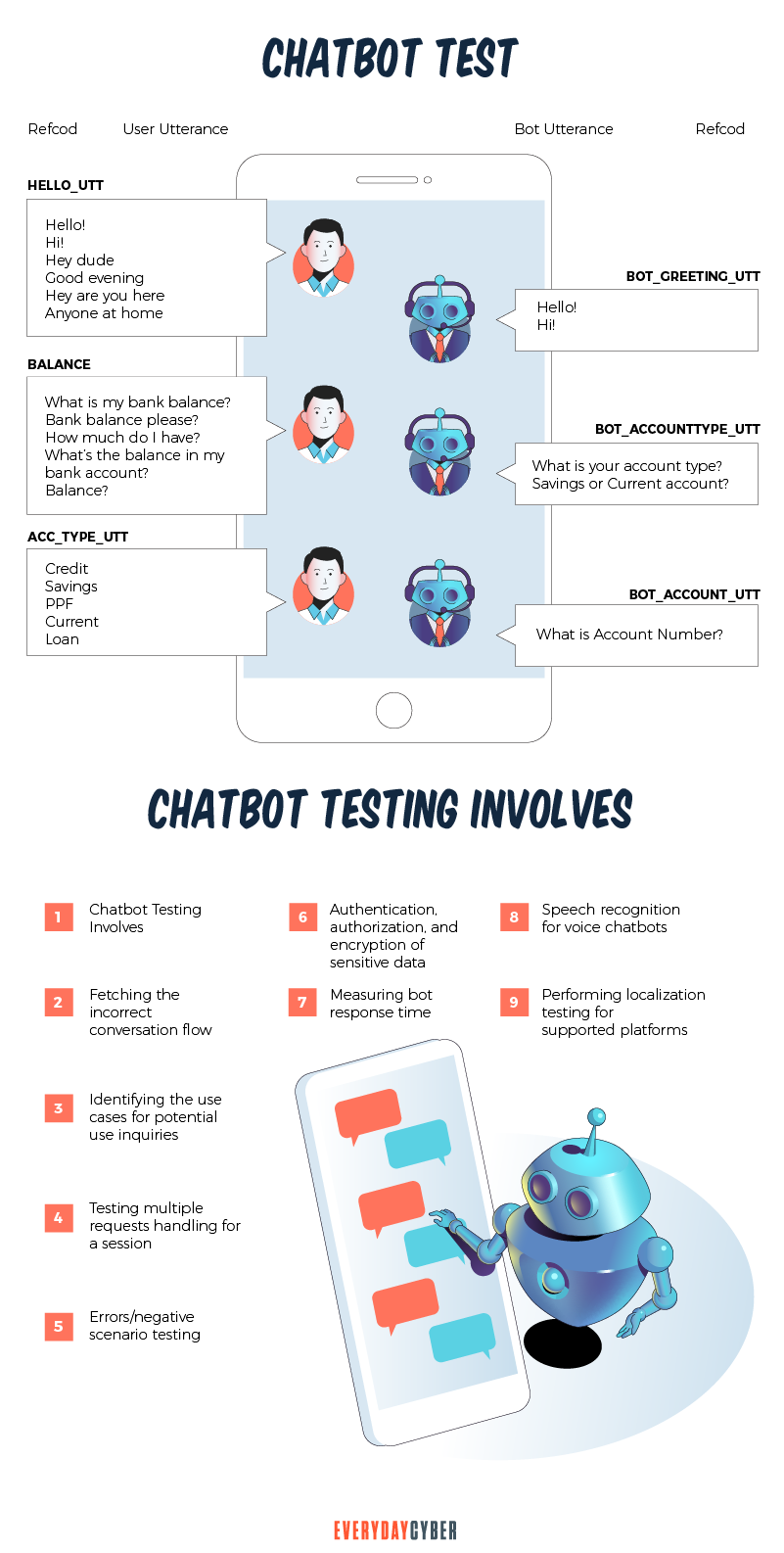
As part of chatbot development, cybersecurity professionals should make it a point to test their chatbot system after its release. So here are some tests you can try:
Penetration testing
This is a technique for determining your chatbot’s vulnerability. It’s also known as “ethical hacking.” It can be done manually by
API security testing
This method involves checking the integrity of your chatbot’s application programming interface. API is a program that facilitates connectivity interface to an application. In short, it allows two applications to talk to each other for more improved chatbot communication.
This is generally performed by
Comprehensive UX testing
A pleasant user experience is usually the outcome of a well-designed technology. It’s a good idea to do your own test if you want to get a thorough understanding of your users’ chatbot interactions. What is it like to interact with your chatbot? Is it acting the way you anticipated it to? Are there any flaws that are obvious?
Our final thoughts. Chatbots, like any other piece of digital technology, are only as safe as you make them. They have the potential to be exploited by hackers as a backdoor. They are, however, as safe and secure as any other customer-facing technology if you are willing to invest in them.
We hope this guide has provided you some helpful insight into the processes you can use to keep your chatbot system safe.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
7 ways to secure your home office
People working from home perform most of their tasks online. They are now more exposed to cyber attacks than ever before. Cyber criminals see a great opportunity in the massive growth in working from home and the vulnerabilities of home office security.
What is DNS Hijacking?
DNS hijacking is no laughing matter. It is a serious security threat that is consuming the cyber world. The critical role of DNS for network security has made a primary target for facilitating mass data theft.
Why should you use a Password Manager?
How many passwords do you have? Did you know the average Internet user has 100 passwords. That's a lot of passwords to remember on a daily basis. How do manage all those password effectively - a password manager.
Should you use a VPN?
The Internet can be a treacherous place. One of the most important measures you can take while online is to use a virtual private network (VPN), whether you’re at your workplace, on the go, or at home. VPNs keep your online activities secure and private, especially on public Wi-Fi. But VPNs can do so much more.
12 Ways to Help Older Adults Stay Safe Online These Days
Seniors, like everyone else, have special vulnerabilities in addition to the common Internet risks. They have specific characteristics that make them vulnerable online, particularly to online fraud. Isolation and lockdowns caused by the pandemic have forced seniors to embrace technology like never before. Here are 12 ways to key seniors safe online.
A Step-by-Step Process for Creating an SMB Cybersecurity Plan
Failing to plan is a plan to fail. The vulnerability of your small business's digital infrastructure is dramatically increased without a sound cyber security plan. Business plans help achieve desirable outcomes. You don't want to be a cyber attack victim, so build a plan.



