Our homes today have a mountain of smart devices that demand internet connectivity. They include our computers, tablets, phones, refrigerators, TVs, or baby monitors. Our increased reliance on the internet to link all of these devices has opened the door to various threats and
Many homeowners are just unaware of the

Hackers are cunning, waiting to exploit any
Securing your home Wi-Fi is key to making your smart home safer.
Passwords are good defense systems, but they alone can no longer completely secure our home networks and smart devices. Cyber attacks have grown in sophistication as cyber criminals compete to improve their attack techniques as new technologies emerge.
Home network security is two-pronged
There are two main components to securing your home network.
The first is securing your router. A basic factor to consider is to choose an excellent router with built-in
The second thing to consider is to secure the devices that connect to the network through the router. This applies to both wireless and cable connections.
In this blog post, we share some tips on how you can better protect your home network. We’ve segregated the techniques that apply to your router and those that apply to your connected devices.
Protecting your router
Your router is at the center of your home wireless network.
The majority of wireless networks used by home users are insecure. Some are so vulnerable to attacks that they need to be replaced, or at the very least properly secured.
In a hacker conference in New York, independent computer analyst Michael Horowitz warned, “A compromised router can spy on you.” He went on to say that a router controlled by an attacker can perform a man-in-the-middle assault, change unencrypted data, or redirect users to “evil twin” websites posing as popular webmail or online banking portals.
There are various things that home network administrators can do to ensure that their routers are more secure, regardless of whether they are commercial or consumer-grade. Here are some of them:
1. Update your router’s firmware
Keeping your router’s firmware up to date is smart cybersecurity practice. Hackers can take advantage of weaknesses in older firmware.
Some routers allow users to check for firmware upgrades via the administration interface, and some even offer automatic updates. You can also examine whether there are any updates for your router model on the website of the router manufacturer. Make it a habit to do this every month.
2. Change the default name of your Wi-Fi network
If you want to improve the
Malicious attackers will have a tougher time figuring out what type of router you have if you change your Wi-Fi’s name. If a cybercriminal knows your router’s manufacturer, they’ll be able to figure out what vulnerabilities it has and try to exploit them.
Changing the default name makes it far more difficult for a hacker to figure out what router you have, lowering the risk of an attack. SSID concealing is a function that allows you to keep your network name hidden from the list of persons in your immediate vicinity.
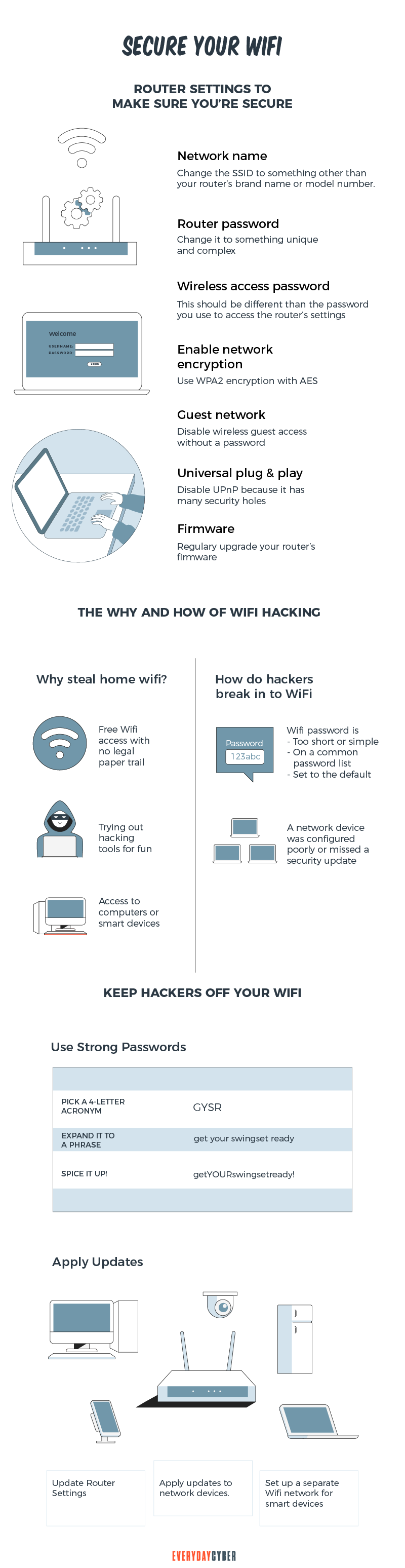
3. Change the default password of your Wi-Fi connection
Wi-Fi providers automatically designate a default password to a home network. Hackers can readily obtain default passwords by searching the internet. They can alter the password to whatever they want, lock the owner out, and hijack the network if they obtain access to it.
By changing the password, attackers will have a harder time gaining access to the network. Hackers use sophisticated software to test thousands of different password combinations. To make it more difficult to crack, use a strong password that incorporates letters, numbers, and symbols.
4. Control router administrator functions
You should control or limit router administrator functions to regulate network usage and protect your network from hackers and viruses. Here are some aspects to consider:
Change your router administrator login credentials
The default credentials on most Wi-Fi routers are “admin” and “password,” which are easy for hostile hackers to crack. To change the administrator credentials, access the router’s settings and change the default credentials to something more difficult to guess.
Make a username that isn’t connected to you in any way, and pair it with a strong password that includes uppercase and lowercase letters, as well as alphanumeric characters.
Disable remote admin access
The majority of routers only let you access their interface through a connected device. Some of them, on the other hand, allow access from remote systems.
Malicious actors won’t be able to access your router’s privacy settings from a device that isn’t connected to your wireless network once you disable remote access.
Limit local admin access
Limiting local admin access to your router is another way to keep an eye on the
Change the default admin IP address
Hackers may easily find default router IP addresses. They can even be found on the internet from time to time. You can modify your router’s address for added

Look for network settings or LAN/DHCP in your router’s admin console. Change your IP address and save your settings. Please take note of the updated address.
It should be enough to only change a handful of numbers. You use the new address to access your router settings once it’s been changed. If you need to change your IP address again for whatever reason, you can reset your router to factory defaults.
5. Activate the highest encryption possible
One of the most effective ways to protect your network data is to use encryption. Encryption scrambles your data or the contents of a message to prevent hackers from deciphering it.
WPA2 is the most secure method of encryption for a home Wi-Fi network. If you have older devices (up to ten years old), they may not be compatible with WPA2. You’ll need to upgrade them for better
Look through your network settings to see if your router employs WPA2 encryption and choose the optimum encryption option.
6. Segment your Wi-Fi network
For IoT devices
It’s a good idea to keep your IoT devices on their own Wi-Fi network. Why? Because the majority of IoT devices have inadequate
A separate connection is a straightforward solution to this problem. Remember to choose a different password for this network so that hackers can’t figure out what your regular Wi-Fi password is.
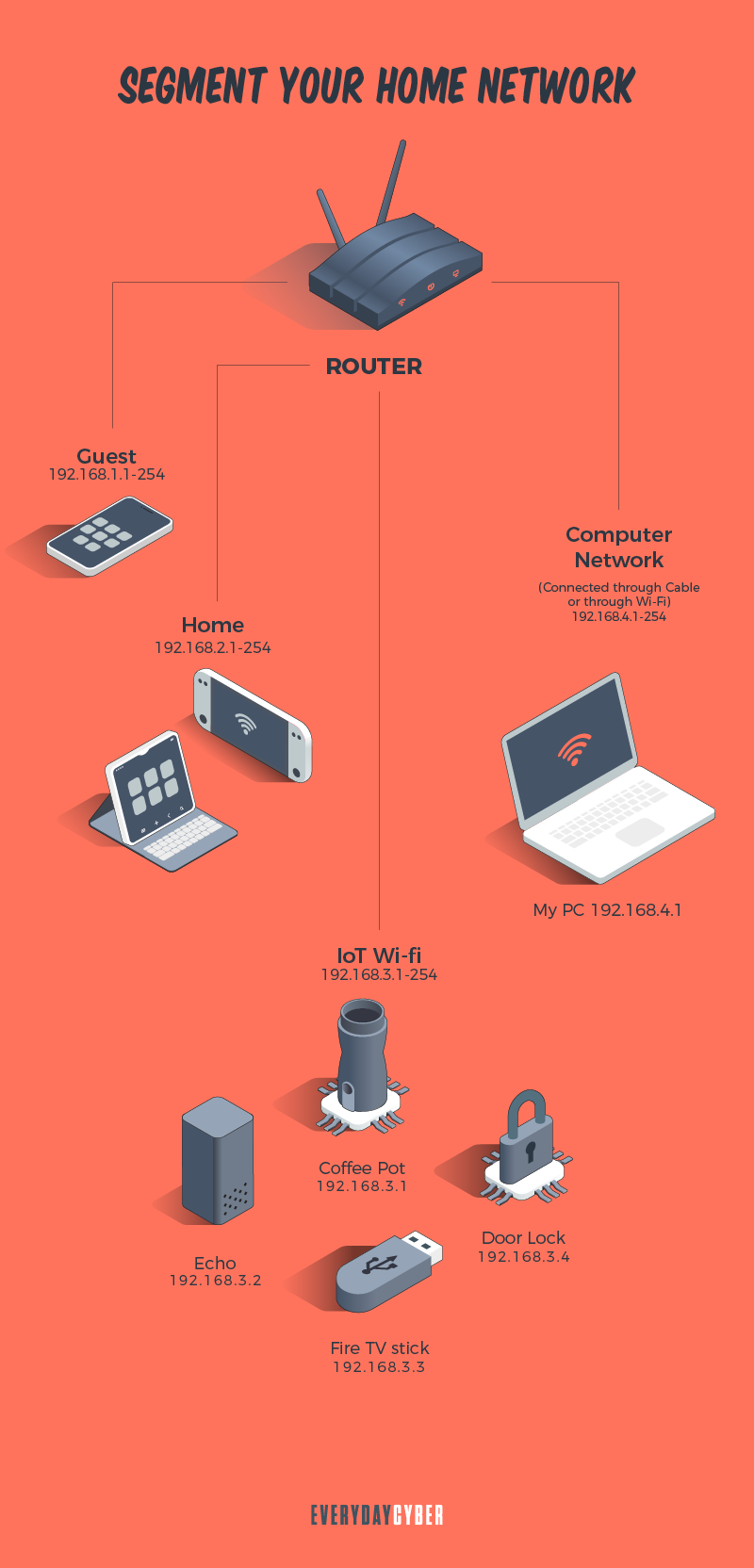
For visitors’ devices
Keep your main Wi-Fi connection private and accessible only to permanent occupants of the house to avoid cyberattacks. Give no one your credentials, whether it’s a neighbor or a close friend. You never know who they share your login information with or under what conditions.
Even if they don’t do it, they could still visit your network with an infected device. This has the potential to infect all of your connected devices. The chance of the threat spreading to every machine connected to your Wi-Fi is reduced when you have a distinct network.
7. Disable Wi-Fi protected setup (WPS)
The WPS feature on your router was created to make it easier for those who aren’t extremely tech-savvy to add new devices to the network. It accomplishes this by reducing the entire process to the click of a single button or PIN code.
WPS is convenient, but it is also quite dangerous. If you leave it turned on, hackers could gain access to your login information in a matter of hours. We strongly suggest you turn it off on your home network.
8. Hide your SSID name
You’ll be asked to create a publicly visible network name called SSID when you first set up your home network. The majority of devices come pre-configured with a manufacturer-assigned network name.
There’s a strong probability your neighbor has a device with the same SSID from the same brand. If both networks are unencrypted, this might become a
SSID concealing is a function that allows you to keep your network name hidden from the list of persons in your immediate vicinity. Changing the default name makes it far more difficult for a hacker to figure out what type of router you have.
9. Implement MAC address filtering
Set the MAC address filtering option to further restrict which devices can connect to your Wi-Fi network. Access your router’s web interface and look for the option MAC Filter, Network Filter, Access Control, or Network Access. It can be found under either the
Only specified MAC addresses will be able to connect to the network if this option is enabled. You can also do ARP Binding, which binds IP and MAC addresses together. This assigns a unique IP to each MAC address, ensuring that the device connects to the same IP every time.
10. Activate all the built-in security features of your router
Most routers include basic and more advanced
There are three main
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) Firewall
Your SPI firewall keeps track of your sessions and ensures that all network traffic is valid. This functionality is enabled by default. So if you want to avoid a cyberattack, leave it that way.
Virtual Private System (VPN)
If you want VPN tunnels that use corresponding protocols to travel via your home network, you should use a
Application Layer Gateway (ALG)
ALG should always be enabled because it allows you to modify application control data protocols that transit via your network.
Protecting your Devices
From your desktop PC, laptop, and smartphone to smart home IoT devices, you can connect practically every gadget in your home to your WiFi.
To keep the home network safe at all times, homeowners must ensure that these devices are well-protected. While it may appear difficult to do this on your own, you don’t need to be a tech whiz to protect your devices. Here are basic
11. Install a virtual private network (VPN)
A
A

12. Use strong antivirus software
Malware is computer code that can harm your computer or laptop, as well as the data stored on it. Inadvertently downloading malware from a malicious email attachment or an infected USB drive, or even visiting a shady website might infect your devices.
Malware can steal your data, encrypt it so you can’t access it, or completely destroy it once it’s on your devices. This is why it’s critical to install strong
13. Implement patch management
Patch management involves testing devices for missing software updates. Patches are created by software firms when they are aware of a known vulnerability in order to prevent hackers from exploiting it to get access to your home network.
Patches are required to keep devices and networks up to date and protect them from
14. Apply Domain Name System (DNS) traffic filtering
DNS filtering is the process of restricting access to specified websites for a specific reason, most commonly content screening. If a website is flagged as malicious, its IP address is blacklisted by a DNS filter, and access to it is blocked. Adult, gambling, productivity sinks, and sites considered to represent a major virus risk are all examples of sites that may be blacklisted.
DNS filtering is vital since it helps reduce the amount of risks to your devices and home network. Effective DNS filtering can prevent up to 88% of internet-borne malware from reaching the network.
Our final thoughts. You should make securing your home network a top priority. We hope that the guide we’ve provided will be useful even for those who aren’t tech-savvy. These techniques aren’t infallible, but they’re a worthy effort that will significantly reduce threat concerns in your home.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is a Rootkit?
Rootkits are nearly invisible and a dangerous type of malware that allows hackers access to computers without the knowledge of the owners. It is designed in such a way that it can remain in a network or on a computer system undetected for an extended period of time.
BEST 10 Tips to Secure your Smart Home Devices
Smart devices are everywhere and rapidly becoming ubiquitous in our lives. Secure them or pay the price.
What is a Keylogger?
Keylogger is a digital surveillance tool. They can track every click, touch, key stroke, download and conversation carried out on the device they are installed on
Why should you use a Password Manager?
How many passwords do you have? Did you know the average Internet user has 100 passwords. That's a lot of passwords to remember on a daily basis. How do manage all those password effectively - a password manager.
What is Two Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a security mechanism in which individuals provide two authentication factors to log on to their account. Using a username and a password to log in to an account is in itself a 2FA. So is withdrawing cash from an ATM using your ATM card and a PIN.
Piggybacking in Plain English: 6 Ways to Keep Your Neighbors from Stealing Your Wi-Fi
Stopping piggybacking all boils down to vigilance and protecting your Wi-Fi with a good VPN, antivirus software, firewall, and security patches.


