Committing deadly sins, again and again, is unforgivable in digital
Let us tell you about the seven deadly cybersecurity sins plaguing small businesses. We will also show real world attacks to highlight their deadliness. We hope this will help you develop robust
1. Using weak passwords
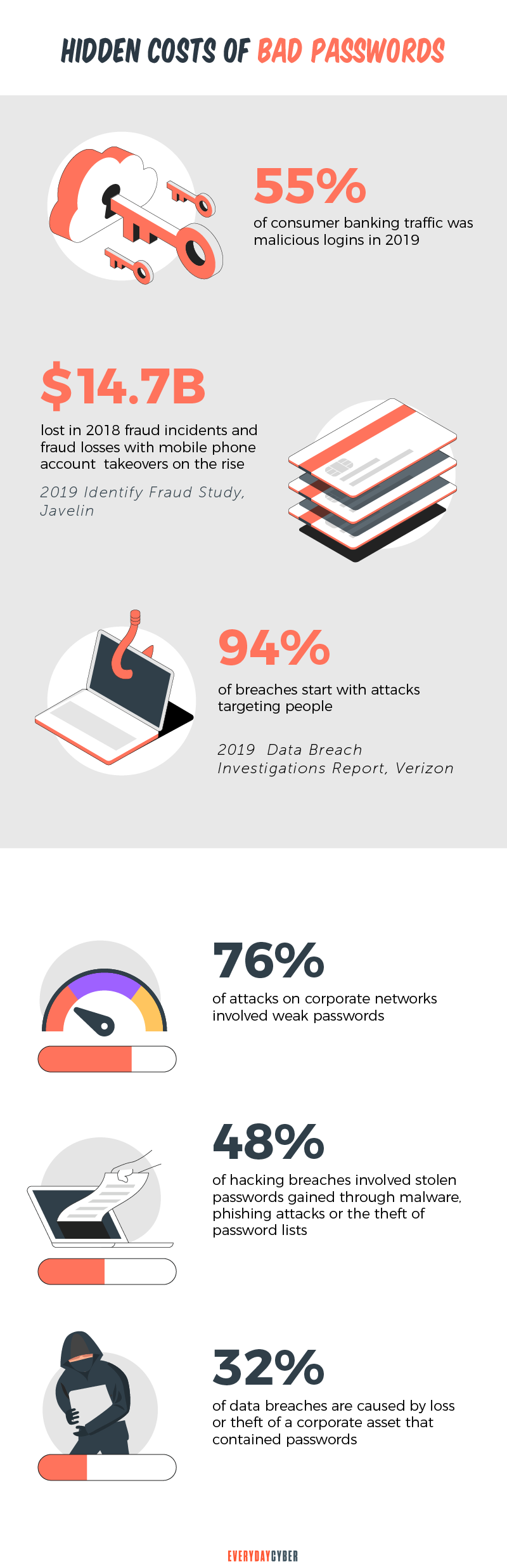
Weak passwords are a recipe for cybersecurity compromise. Think data breaches, account takeovers, and
What are weak passwords? Weak passwords are those that are common, short, and default-based. They could also be anything that can be easily cracked by hackers using brute force. Long passwords are also weak if they contain common words related to the user. Such words can be family information, birth dates, or
Common examples are:
- 1234567, 12345678, 123456789, 1234567890
- Password
- qwerty
- qwertyuiop
- football
- baseball
- abc123
- 111111
- 1qaz2wsx
- starwars
Password mistakes
Related to weak passwords are password mistakes that are equally vulnerable to attacks. Here are some of them:
- Using personally identifiable information
- Using simple chains of characters
- Sharing passwords
- Not changing passwords regularly
- Using the same password on various accounts and sites
Some tips: Avoid personal information. Use long and complex strings of alphanumeric characters. Use unique passwords for each account and segregate personal accounts from work accounts. Never recycle passwords. Consider multi factor authentication.
2. Lack of a systematic backup policy
Not having a backup strategy is one of the seven deadly cyber
These consequences are not guesswork but proven by real-life incidents. Here are a couple of statistics on what is happening on the ground:
Datto: According to a Datto study, the average cost of downtime for large enterprises is $11,600 per minute. More specifically, an hour of downtime costs:
- $8,000 for a small business
- $74,000 for a midsize business
- $700,000 for a large business
Backblaze: The Drive Stats 2020 reported that 93% of hard drives failed in 2020. A hard drive is a component of your computer that stores all your data, from files to software. Companies without a backup system may lose all their data forever.
Some tips: These are alarming real world attacks that need a solid backup strategy. Before developing your backup system, conduct assessments on pertinent
- Vulnerability assessment
- Database assessment
- Asset assessments
- Web application assessment
- Operating system
security assessment - Wireless assessment
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
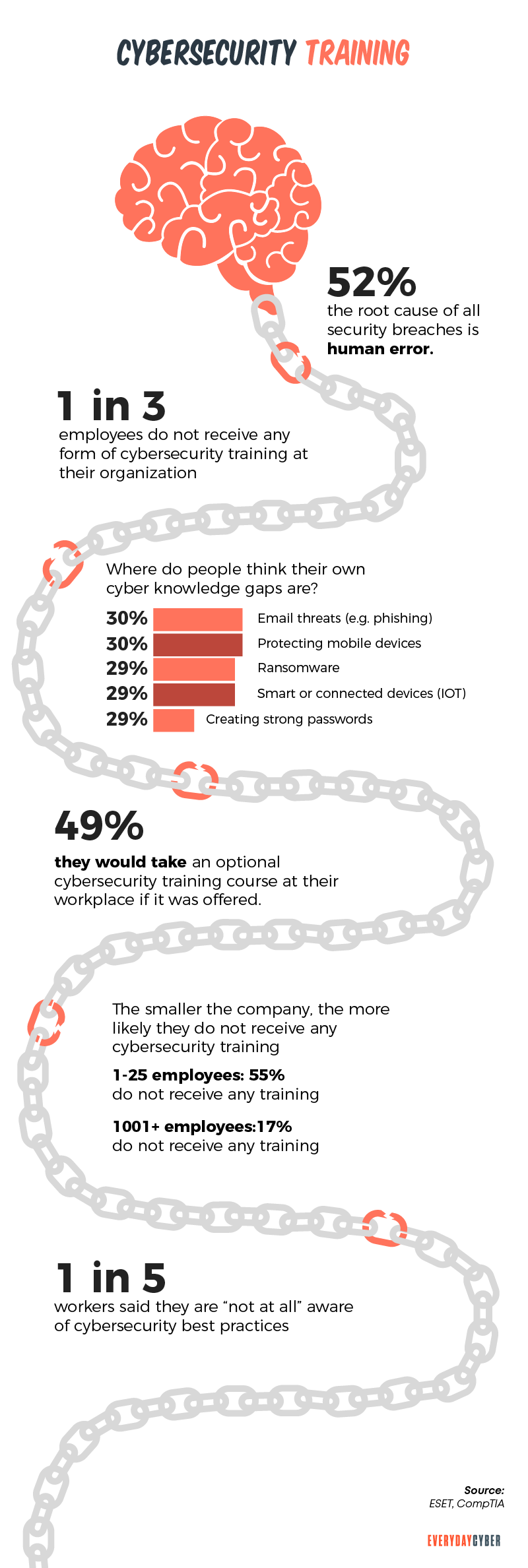
3. Lack of security training for employees
What is the role of the human factor in cybersecurity? When given the best

Employees are the biggest source of immediate and potential threats. Axelos’ RESILIA report revealed that 45% of attacks are caused by unintentional errors. The intentional attacks were a little lower at 40%.
Some tips: Most breaches are caused by human error regardless of a company’s size. Make your training programs effective and meant for real-life situations. Design them to be interactive and engaging for both humans and machines.
4. Taking cybersecurity for granted
In the past, threat actors preferred to attack enterprise-level businesses. They targeted them for their deeper pockets and the wealth of data they keep. But that preference has shifted to include small businesses in recent years.
Why then are small businesses not taking network
SolarWinds published its Public Sector Cybersecurity Survey Report 2020. The report says that 87% of businesses had average or better cyber
There seems to be a gap between policy and application. What businesses say about the state of their cybersecurity is one thing. What’s happening on the ground is another.
The figures are at odds. Why? Most small businesses exhibit one common characteristic – overconfidence. Overconfidence leads to other shortcomings, such as:
- Enforcing policies only occasionally
- Neglecting end users
- Being complacent
- Being stubborn
5. Being more reactive than proactive to cybersecurity
Both reactive and proactive cyber
What is reactive cybersecurity?
Reactive cybersecurity involves responding to an attack during or after it happens. The visible signals that prompt the IT
- Confusing database requests
- Permission and authentication issue
- Malicious software activation.
After discovering a data breach or cybersecurity compromise, the
- Investigate the root cause of the attack.
- Check the anti-malware software. Replace it with a more resilient one.
- Clean up the malware.
- Patch identified vulnerabilities.
- Rapidly address potential vulnerabilities with the Highly Adaptive Cybersecurity Services HACS. It is available through the Multiple Award Schedule (MAS) Information Technology.
- Introduce new
security features. - Advise government agencies or the federal government.
- Consider other technology solution options.
What is proactive cybersecurity?
Proactive
- Cyber hunt activities
- Penetration testing
- Proactive intrusion detection
- Security testing
- Security awareness training
- Security architecture review
- Proactive adaption of appropriate mitigation countermeasures before attacks happen
Some tips: Reactive cybersecurity can be beneficial after an attack. But it must be paired with a proactive strategy. Being proactive helps your organization identify and detect potential threats before they happen. Cyber hunt activities detect risky activities that have evaded detection by existing tools. It also helps you respond and recover from an attack more effectively. It lowers your risk from data breaches.
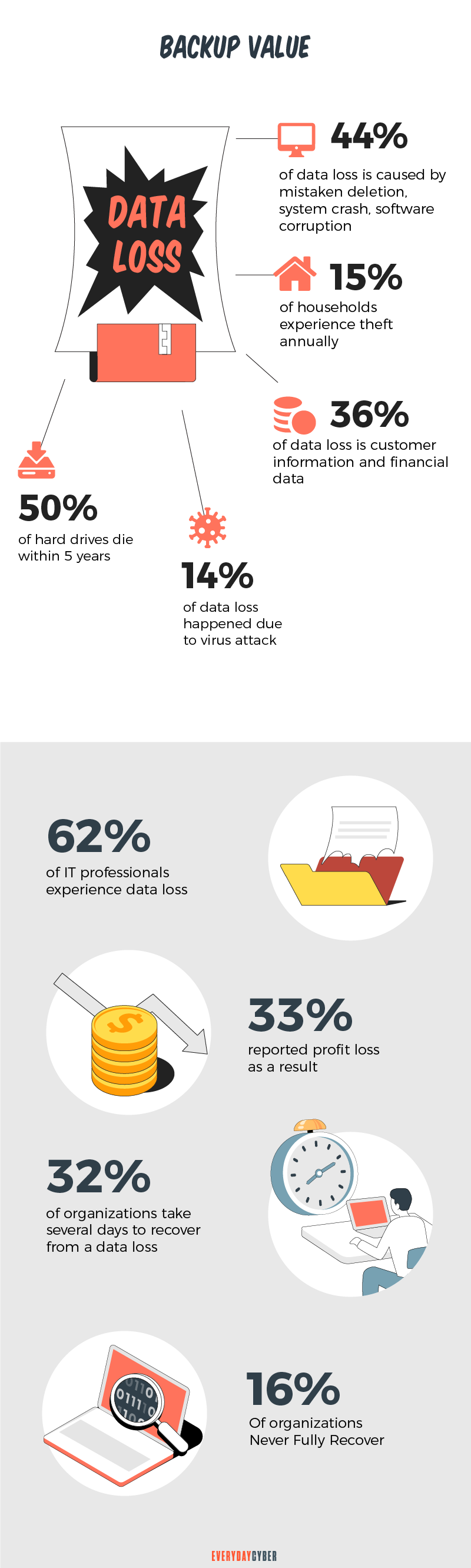
6. Being oblivious to uncontrolled data
Many businesses appear to be ignorant of the risks of uncontrolled data. Uncontrolled data can lead to catastrophic data loss and costly lawsuits. Worse, it can bring businesses down.
The consequences of data loss are not speculation but hard fact proven time after time.
The University of Texas found that:
- 94% of businesses don’t recover from catastrophic data loss
- 51% will close within two years
- 43% will never recover
Some tips: Uncontrolled data could compromise your whole network. Strict physical
7. Not having a cybersecurity policy in place
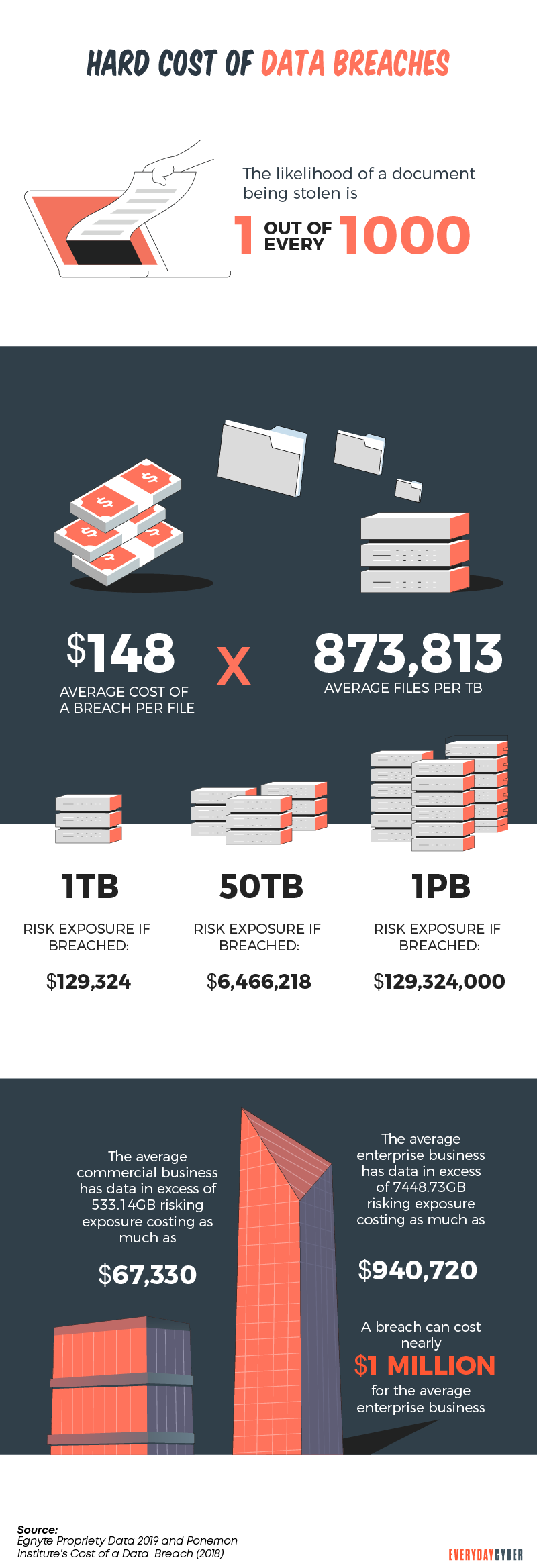
Threat actors are becoming relentless in launching cybersecurity breaches. They’re always looking for potential vulnerabilities to exploit in increasingly connected devices. Without a policy, you’re leaving customer data and other sensitive information vulnerable.
Here are the greatest impacts of a weak or non-existent cyber
Loss of customers and revenue
You can’t blame customers if 57% of them hold you, rather than hackers, responsible for their stolen data. They entrusted their information expecting you will protect it. Once you breach this trust, 78% of them would stop interacting with you online. And 36% would be gone forever, including potential revenue from them.
Loss of intellectual property
A weak cyber
Damage to your brand reputation
When a data breach occurs, the media goes to work. Large-scale breaches make the national news. Small-scale ones find their way to local newspapers and social media. The news will always reach your stakeholders. This can damage your brand reputation.
Risk of losing your business
Unlike large enterprises, small businesses have limited
Some tips: Hackers are getting bolder and more sophisticated in their attacks. Businesses must double down in crafting and implementing a resilient cybersecurity policy. Use highly adaptive cybersecurity services to test high priority IT systems.
All good cybersecurity policies include best practices like:
- Defense measures and controls
- Certifications
- Monitoring
- Audit reporting
- Compliance of everybody from the CEO down to the lowest ranking employee
- Adapting appropriate mitigation countermeasures
- Partnering with technically evaluated cybersecurity services
- Considering cybersecurity services or pre vetted support services to help your
security team - Making sure to inform federal agencies of breach incidents
If you have committed any of the seven deadly sins we outlined, you’re not hopeless. Try to repent and atone for those sins. Adhere to cybersecurity best practices and the tips we shared.
To summarize those tips:
1. Use strong passwords.
A strong password is difficult to guess. It should be at least 8 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Never use the same password for more than one account.
2. Adapt a systematic backup policy.
A backup policy must be part of your business continuity and disaster recovery plan. By backing up all your critical data on schedule, you cut the impact of a data loss event. Schedule regular backups of your data to a secure location, such as an off-site data center.
3. Provide security training for your employees.
Educating employees to identify and respond to potential threats reduces the risk of a breach. Some best practices for providing cybersecurity training for employees include:
- Creating a policy for acceptable use of technology
- Educating employees on how to identify phishing emails
- Teaching employees how to use strong passwords
- Instructing employees on how to protect their personal information
- Explaining the consequences of violating the company’s cybersecurity policy
- Encouraging employees to report any suspicious activity
4. Create a cybersecurity strategy
A cybersecurity strategy outlines how you will protect your networks and systems. It identifies the risks you face and the steps you need to take to mitigate those risks. It also includes procedures for responding to cyber incidents and for recovering from them.
5. Take control of your data
There are a lot of things to think about when it comes to data. What information do you want to keep private and what do you want to share? What’s the best way to store and back up your data? How can you keep your devices safe from viruses and hackers? Taking control of your data means thinking about these things and more. It means being aware of the risks and taking steps to protect yourself and your information. It also means being choosy about what information you share and with whom.
6. Put a cybersecurity policy in place
A cybersecurity policy includes guidelines for:
- employee behavior online
- procedures for reporting cyber incidents
- and a plan for responding to attacks.
It’s important to keep it up-to-date, as the threat landscape changes all the time.
7. Go for adaptive cybersecurity services
One of the most important aspects of cybersecurity is the ability to adapt to new threats as they emerge. This is where adaptive cybersecurity services come in. These services track your network for new threats and adapt your
9. Do vulnerability assessments regularly
By identifying vulnerabilities, you can fix them before someone else takes advantage of them. Vulnerabilities are discovered all the time. So you must do assessments regularly to keep up with them.
10. Perform security testing regularly
Security testing must be done periodically to ensure the system remains secure. It’s important to stay up to date with the latest
11. Check your systems security engineering design
To identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, you need a review of the system design. This includes an analysis of the system architecture and the design of the
12 Opt for pre-vetted support services to back your security team
Pre-vetted support services can help your
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is a Website Security Certificate?
A website security certificate is a digital certificate that asserts the identity of a website. It’s a virtual file approved by an industry-trusted third-party called a certificate authority (CA)
What is Malware?
Malware or “malicious software” is a cybersecurity term used to describe software that steals your data, spies on you, damages your devices, and generally causes chaos and destruction.
What is a Back Door Threat?
In cybersecurity, a Back Door Threat enables a hacker to gain unauthorized access to a computer or digital device at any time.
What is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT)?
A remote access Trojan is a software used by hackers to gain unauthorized access and remote control on a user’s computer or mobile device, including mouse and keyboard manipulation.
5 Biggest Cybersecurity Mistake SMBs do
Small and midsize companies can’t afford to learn cybersecurity haphazardly while cyberattacks are steadily rising. If you’re a decision-maker, you can’t ignore the 424% increase in cyber breaches in 2021.
10 Cybersecurity Trends for Small Businesses in 2022
Knowing the latest cybersecurity trends spells the difference between keeping your business safe and opening it up to cyber attackers.